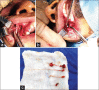
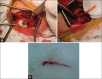
Peripheral Neurectomy for Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Report of Seventeen Cases and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 34268152
- PMCID: PMC8244708
- DOI: 10.4103/ajns.AJNS_361_20
Peripheral Neurectomy for Trigeminal Neuralgia: A Report of Seventeen Cases and Review of the Literature
Abstract
Background: Surgical intervention for trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is indicated if there is a failure of the medical treatment. Peripheral neurectomy is one of the oldest surgical procedures for TN.
Objective: The aim is to evaluate the clinical outcome and the recurrence rate following peripheral neurectomy for the management of TN.
Patients and methods: This was a retrospective cohort study of 17 patients with classical TN treated by peripheral neurectomy. The visual analogue scale (VAS) was used for pain assessment preoperatively and during the follow-up period. The outcome of surgery was graded as a marked, moderate, or mild improvement. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used for the time to recurrence to predict the probability of recurrence at any given time following the procedure.
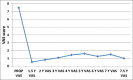
Results: The mean pain-free interval was 29.3 ± 16.3 months. At 2 and 5 years of the follow-up period, the mean VAS improved significantly (P < 0.001 and P = 0.042 respectively). Thirteen patients had marked improvement of pain. There was recurrence of pain in 4 patients (23.5%). By Kaplan-Meier analysis, the survival rate without recurrence at 2, 3, 4, and 5 years following the procedure were 92.9%, 79.6%, 59.7%, and 29.8%, respectively. The mean preoperative Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale-Anxiety and Depression scores significantly improved on the last follow-up visit following the procedure (P < 0.001 for both).
Conclusion: Peripheral neurectomy provides short to medium-term good pain control for patients with TN. The preoperative severity of pain, anxiety, and depression levels improved markedly after the procedure.
Keywords: Inferior alveolar; infraorbital nerve; peripheral neurectomy; trigeminal neuralgia.
Copyright: © 2021 Asian Journal of Neurosurgery.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Okeson JP. The classification of orofacial pains. Oral Maxillofacial Surg Clin N Am. 2008;20:133–44. - PubMed
-
- Jeyaraj P. Efficacy of peripheral neurectomy in the management of refractory cases of trigeminal neuralgia. Otolaryngology. 2019;8:178.
-
- Koopman JS, Dieleman JP, Huygen FJ, de Mos M, Martin CG, Sturkenboom MC. Incidence of facial pain in the general population. Pain. 2009;147:122–7. - PubMed
-
- Scrivani SJ, Mathews ES, Maciewicz RJ. Trigeminal neuralgia. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005;100:527–38. - PubMed

