The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on socio-economic and sustainability
- PMID: 34268692
- PMCID: PMC8282265
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-021-14986-0
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on socio-economic and sustainability
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on socio-economic and sustainability.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025 Jan;32(4):2165. doi: 10.1007/s11356-025-35926-2. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025. PMID: 39789413 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
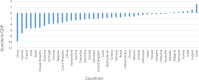
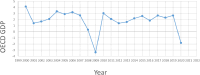
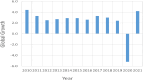
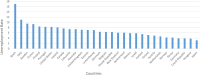
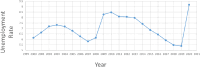
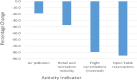
The COVID-19 pandemic has adversely affected the lives of people around the world in millions of ways . Due to this severe epidemic, all countries in the world have been affected by all aspects, mainly economic. It is widely discussed that the COVID-19 outbreak has affected the world economy. When considering this dimension, this study aims to examine the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the world economy, socio-economics, and sustainability. In addition, the research focuses on multiple aspects of social well-being during the pandemic, such as employment, poverty, the status of women, food security, and global trade. To this end, the study used time series and cross-sectional analysis of the data. The second-hand data used in this study comes from the websites of major international organizations. From the analysis of secondary data, the conclusion of this article is that the impact of the pandemic is huge. The main finding of the thesis is that the social economy is affected by the pandemic, causing huge losses in terms of economic well-being and social capital.
Keywords: Employment; Pandemic; Social economy; Sustainability; coronavirus disease; food safety; poor.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Adams-Prassl A, Boneva T, Golin M, Rauh C (2020) Inequality in the impact of the coronavirus shock: new survey evidence for the UK. CEPR Discuss Pap 14665:15
-
- Alauddin M (2016) The rise of rural non-farm sector in Bangladesh: a distinct socio-economic transformation. AAFR 2(1):189–203
-
- Back-of-the-Envelope Estimates of Next Quarter’s Unemployment Rate. (2020). Available Online: https://www.stlouisfed.org/on-the-economy/2020/march/back-envelope-estim... (accessed on 25 June 2020).
-
- Barro RJ; Weng J (2020). The coronavirus and the Great Influenza Pandemic: lessons from the “Spanish Flu” for the coronavirus’s potential effects on mortality and economic activity. NBER Work. Pap. Ser.Vol. 25.
-
- COVID-19: (2020a). Putting people first. Available Online: https://www.unwto.org/tourism-covid-19 (accessed on 25 June 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- GJE1320136/Heilongjiang Provincial Education Science Planning
- GBB1318076./Heilongjiang Education and Science
- JD2017021./Heilongjiang Economic and Social Development Key Research Project
- 2018-KYYWF-0594/Heilongjiang Provincial University Basic Scientific Research
- 19FXB039./Heilongjiang Philosophy and Social Science Research
- 17GLB026./Heilongjiang Philosophy and Social Science Research
- DQXN201612./Harbin Medical University
- DQCTWH201801./Harbin Medical University
- DQCTWH201802./Harbin Medical University
- YF16-Y02./Sichuan Provincial Philosophy and Social Sciences Key Research
- DSGB2019035./Daqing philosophy and social science planning research
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical