The prevalence of multimorbidity in primary care: a comparison of two definitions of multimorbidity with two different lists of chronic conditions in Singapore
- PMID: 34271890
- PMCID: PMC8283957
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-021-11464-7
The prevalence of multimorbidity in primary care: a comparison of two definitions of multimorbidity with two different lists of chronic conditions in Singapore
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of multimorbidity varies widely due to the lack of consensus in defining multimorbidity. This study aimed to measure the prevalence of multimorbidity in a primary care setting using two definitions of multimorbidity with two different lists of chronic conditions.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study of 787,446 patients, aged 0 to 99 years, who consulted a family physician between July 2015 to June 2016. Multimorbidity was defined as 'two or more' (MM2+) or 'three or more' (MM3+) chronic conditions using the Fortin list and Chronic Disease Management Program (CDMP) list of chronic conditions. Crude and standardised prevalence rates were reported, and the corresponding age, sex or ethnic-stratified standardised prevalence rates were adjusted to the local population census.
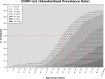
Results: The number of patients with multimorbidity increased with age. Age-sex-ethnicity standardised prevalence rates of multimorbidity using MM2+ and MM3+ for Fortin list (25.9, 17.2%) were higher than those for CDMP list (22.0%; 12.4%). Sex-stratified, age-ethnicity standardised prevalence rates for MM2+ and MM3+ were consistently higher in males compared to females for both lists. Chinese and Indians have the highest standardised prevalence rates among the four ethnicities using MM2+ and MM3+ respectively.
Conclusions: MM3+ was better at identifying a smaller number of patients with multimorbidity requiring higher needs compared to MM2+. Using the Fortin list seemed more appropriate than the CDMP list because the chronic conditions in Fortin's list were more commonly seen in primary care. A consistent definition of multimorbidity will help researchers and clinicians to understand the epidemiology of multimorbidity better.
Keywords: Age; Ethnicity; Multimorbidity; Prevalence; Primary care; Sex.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ageing and health. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health. Accessed 8 Nov 2020.
-
- Violan C, Foguet-Boreu Q, Flores-Mateo G, Salisbury C, Blom J, Freitag M, Glynn L, Muth C, Valderas JM. Prevalence, determinants and patterns of multimorbidity in primary care: a systematic review of observational studies. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e102149. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102149. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boyd CM, Fortin M. Future of multimorbidity research: how should understanding of multimorbidity inform health system design? Public Health Rev. 2010;32(2):451–474. doi: 10.1007/BF03391611. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources