The effectiveness of Kangaroo Mother Care in hospitalization period of preterm and low birth weight infants: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34274324
- PMCID: PMC9432036
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jped.2021.06.004
The effectiveness of Kangaroo Mother Care in hospitalization period of preterm and low birth weight infants: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness of kangaroo mother care (KMC) in reducing the length of hospital stay of preterm and/or low birth weight infants.
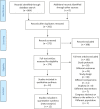
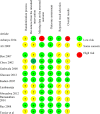
Source: Cochrane Library, Pubmed, Embase, LILACS, and Scielo. Randomized clinical trials without time or language limit were included. The intervention was the KMC in preterm and/or low birth weight infants born in health facilities compared to conventional care. The article selection was performed by a pair of reviewers independently. The methodological quality assessment was performed using the tool Risk of Bias 2.
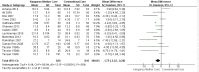
Summary of the findings: Eight hundred and sixty-four citations were identified and 12 were selected for data extraction. There was a reduction in the length of hospital stay in days in the KMC group compared to the conventional care group, with a statistically significant difference (MD -1.75, 95% CI -3.22 to -0.28). The subgroup that underwent the intervention for more than six hours daily did not show a statistical difference for the length of hospital stay outcome (MD -0.79, 95% CI -2.52 to 0.90), while the subgroup that underwent the intervention for less than six hours daily showed a reduction in this outcome with a statistically significant difference (MD -4.66, 95% CI -7.15 to -2.17).
Conclusions: KMC is a safe and low-cost intervention that has been shown to be effective in reducing the length of hospital stay of preterm and/or low birth weight infants.
Keywords: Infant, Premature; Infant, low birth weight; Kangaroo-Mother Care Method.
Copyright © 2021 Sociedade Brasileira de Pediatria. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. Survive and thrive: transforming care for every small and sick newborn - key findings.www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/documents/care-small-sick-newborns... [cited 2019 Abr 30]. Available from:
-
- Toma TS. From intuition to the public policies: the journey aimed to the incorporation of the Kangaroo Method (Método Canguru) for the care of low weight newborns. BIS Bol Inst Saúde. 2012;13:1231–1238.
-
- Fundación Canguro y Departamento de Epidemiología Clínica y Bioestadística Facultad de Medicina – Pontificia Universidade Javeriana. Guías de práctica basadas en evidencia para la óptima utilización del Método Madre Canguro em el recién nacido pretérmino y/o de bajo peso al nacer. 2007 [cited 2019 Mar 19]. Available from: www.quenoosseparen.info/documentos/guias_evidencia.pdf
-
- Nyqvist KH, Expert Group of the International Network on Kangaroo Mother Care. Anderson GC, Bergman N, Cattaneo A, Charpak N, et al. State of the art and recommendations. Kangaroo mother care: application in a high-tech environment. Acta Paediatr. 2010;99:812–819. - PubMed
-
- Conde-Agudelo A, Belizán JM, Diaz-Rossello J. Kangaroo mother care to reduce morbidity and mortality in low birthweight infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(3) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

