Rhabdomyolysis: Revisited
- PMID: 34276082
- PMCID: PMC8278949
Rhabdomyolysis: Revisited
Abstract
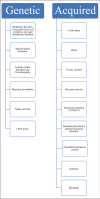
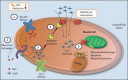
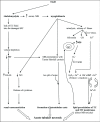
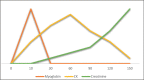
Rhabdomyolysis (RML) is a pathological entity characterized by symptoms of myalgia, weakness and dark urine (which is often not present) resulting in respiratory failure and altered mental status. Laboratory testing for myoglobinuria is pathognomonic but so often not present during the time of testing that serum creatine kinase should always be sent when the diagnosis is suspected. Kidney injury from RML progresses through multiform pathways resulting in acute tubular necrosis. Early treatment (ideally<6 hoursfrom onset) is needed with volume expansion of all non-overloaded patients along with avoidance of nephrotoxins. There is insufficient data to recommend any specific fluid. The mortality rate ranges from 10% to up to 50% with severe AKI, so high index of suspicion and screening should be in care plan of seriously ill patients at risk for RML.
Keywords: Rhabdomyolysis; acute kidney injury; pathophysiology; treatment.
Copyright © 2021 Ulster Medical Society.
Figures

References
-
- Stahl K, Rastelli E, Schoser B. A systematic review on the definition of rhabdomyolysis. J Neurol. 2020;267(4):877–82. - PubMed
-
- Navin TR, Hager WD. Creatine kinase MB isoenzyme in the evaluation of myocardial infarction. Curr Probl Cardiol. 1979;3(12):1–32. - PubMed
-
- Nass RD, Sassen R, Elger CE, Surges R. The role of postictal laboratory blood analyses in the diagnosis and prognosis of seizures. Seizure. 2017;47:51–65. - PubMed
-
- Rutecki GW, Ognibene AJ, Geib JD. Rhabdomyolysis in antiquity. From ancient descriptions to scientific explication. Pharos Alpha Omega Alpha-Honor Med Soc. 1998;61(2):18–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
