Model-Based Meta-Analysis in Psoriasis: A Quantitative Comparison of Biologics and Small Targeted Molecules
- PMID: 34276352
- PMCID: PMC8281289
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.586827
Model-Based Meta-Analysis in Psoriasis: A Quantitative Comparison of Biologics and Small Targeted Molecules
Abstract
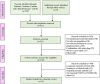
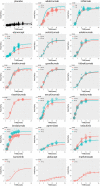
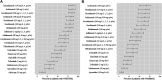
Background: The response time-course information of biologics and small targeted molecules for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis which helps clinicians to understand the onset of action and maintenance of effect are unclear. Quantitative information about the efficacy comparation of different systemic agents are needed. Methods: Model-based meta-analysis was conducted and longitudinal models were developed by applying two clinical end points commonly reported in the clinical trials of psoriasis: the proportion of patients achieving ≥75% reduction from baseline Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI75) and the proportion of patients achieving ≥90% reduction from baseline Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score (PASI90). Results: A total of 80 trials of thirteen biological agents and four small targeted molecules covering 235 treatment arms and 40323 patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis were included in this analysis. The drugs were divided into five classes of biologics and three classes of small molecules. Two longitudinal models of PASI75 and PASI90 were used to describe the time-varying drug effect and dose-effect relationship. The typical response-time courses for PASI75 and PASI90 increased over time and finally reached to the platform. For PASI75 end point at week 12, of all the therapeutic drugs, risankizumab administered as 150 mg at week 0, week 4, and q12w showed the most efficacious with PASI75 was 85.95% (95%CI, 75.71-92.60%), followed by ixekizumab administered as 160 mg at week 0, and q4w with PASI75 was 85.9% (95%CI, 76.12-92.79%). As for PASI90 end point at week 12, ixekizumab 160 mg at week 0, and q4w showed the greatest percentage of person achieved PASI90 (67.2%; 95%CI, 49.91-77.2%), followed by risankizumab 150 mg at week 0, week 4, and q12w (65.5%; 95%CI, 47.8-75.7%). What's more, the risankizumab provided the highest response of PASI90 at week 16 and week 24. Conclusions: This study provided a quantitative efficacy comparation of 17 systemic agents for psoriasis in term of efficacy only and that safety was not considered. Risankizumab and ixekizumab showed superiority for both the two end points.
Keywords: biologics; efficacy comparation; model-based meta-analysis; moderate to severe psoriasis; small targeted molecules.
Copyright © 2021 He, Wu, Zhang, Zhang, Sun, Zhao and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Barker J., Hoffmann M., Wozel G., Ortonne J. P., Zheng H., van Hoogstraten H., et al. (2011). Efficacy and Safety of Infliximab vs. Methotrexate in Patients with Moderate-To-Severe Plaque Psoriasis: Results of an Open-Label, Active-Controlled, Randomized Trial (RESTORE1). Br. J. Dermatol. 165, 1109–1117. 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10615.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blauvelt A., Papp K. A., Griffiths C. E., Randazzo B., Wasfi Y., Shen Y. K., et al. (2017). Efficacy and Safety of Guselkumab, an Anti-interleukin-23 Monoclonal Antibody, Compared with Adalimumab for the Continuous Treatment of Patients with Moderate to Severe Psoriasis: Results from the Phase III, Double-Blinded, Placebo- and Active Comparator-Controlled VOYAGE 1 Trial. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 76, 405–417. 10.1016/j.jaad.2016.11.041 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cai L., Gu J., Zheng J., Zheng M., Wang G., Xi L. Y., et al. (2017). Efficacy and Safety of Adalimumab in Chinese Patients with Moderate-To-Severe Plaque Psoriasis: Results from a Phase 3, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 31, 89–95. 10.1111/jdv.13746 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

