Association Between Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase, Total Bilirubin and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Chinese Women
- PMID: 34276670
- PMCID: PMC8277571
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.682400
Association Between Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase, Total Bilirubin and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Chinese Women
Abstract
Background: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) affects many organs and systems of the human organism, at present, its specific pathogenesis is not completely clear, but inflammation is considered to be an important factor involved in the pathogenesis and progression of SLE. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) and total bilirubin (TBIL) have different effects on inflammation: GGT has pro-inflammatory effects, on the contrary, TBIL has anti-inflammatory effects. Study has found that GGT and TBIL play opposite roles in metabolic diseases. However, the roles of them in SLE are unknown. Meanwhile, the relationship between GGT and SLE also remains unexplored.
Method: We recruited 341 SLE patients and 332 healthy individuals in Liaocheng People's Hospital from August 2018 to May 2019. We diagnosed SLE using 2019 revised American College of Rheumatology (ACR) SLE criteria, and modeled the study outcomes using logistic regression to explore the respective relationship between GGT, TBIL and SLE. We also analyzed the interaction of GGT and TBIL in the progression of SLE.
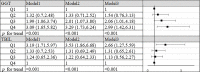
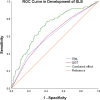
Results: We found that the levels of CRP, IL-6 and TNF-α in the aggravated group were significantly higher than those in the unaggravated group, the levels of C3 and C4 in the aggravated group were significantly lower than those in the unaggravated group. According to Spearman correlation analysis, GGT is proportional to CRP (rs=0.417) and IL-6 (rs=0.412), inversely proportional to C3 (rs=-0.177) and C4 (rs=0.-132). TBIL was inversely proportional to CRP (rs=-0.328) and TNF(rs=-0.360), and positively proportional to C3 (rs=0.174) and C4 (rs=0.172). In the fully adjusted model, compared to the lowest quartile, the highest quartile of GGT exhibited a positive association with the risk of SLE aggravation (OR=2.99, 95% CI: 1.42-6.31, P<0.001). At the same time, compared to the highest quartile, the quartile lowest of TBIL exhibited a positive association with the risk of SLE aggravation (OR=2.66, 95% CI: 1.27-5.59, P<0.001) in the fully adjusted model. Through interaction analysis, we found that women with high GGT levels had an increased risk of SLE aggravation when they had a low level of TBIL (OR=3.68, 95% CI: 1.51-9.01, for women with Q1 TBIL and Q4 GGT compared to women with Q2-Q4 TBIL and Q1-Q3 GGT, P for interaction <0.001), the combined AUC value (AUCCOMBINED=0.711) of high GGT level and TBIL were higher than their respective values (AUCGGT=0.612, AUCTBIL=0.614).
Conclusion: We found that the effects of GGT and TBIL in the progression of SLE are opposite. High GGT level might be a risk factor for SLE aggravation, as GGT levels increased, so did the risk of SLE aggravation. At the same time, we found that low TBIL level might be a risk factor for SLE aggravation. Moreover, high GGT level and low TBIL level had a subadditive effect on the increased risk of SLE aggravation.
Keywords: case-control study; diagnostic marker; female population; gamma-glutamyl transferase; systemic lupus erythematosus; total bilirubin.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Tang, Shi, Ji, Chen, Chen, Wang, Wang, Wang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Relationship between bilirubin and systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Dec;11(12):e1115. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1115. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 38156396 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and indirect bilirubin may participate in systemic inflammation of patients with psoriatic arthritis.Adv Rheumatol. 2023 Oct 30;63(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s42358-023-00334-y. Adv Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37904193
-
Bilirubin levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: increased or decreased?Rheumatol Int. 2012 Aug;32(8):2423-30. doi: 10.1007/s00296-011-1977-9. Epub 2011 Jun 21. Rheumatol Int. 2012. PMID: 21691742
-
Serum Cyr61 is associated with clinical disease activity and inflammation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 May;94(19):e834. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000834. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 25984669 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical disease activity and flare in SLE: Current concepts and novel biomarkers.J Autoimmun. 2021 May;119:102615. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102615. Epub 2021 Feb 22. J Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 33631651 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic analysis of the relationship between systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity and psychosocial support.Front Psychol. 2024 Aug 14;15:1433868. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1433868. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39205979 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between Total Bilirubin, Total Bilirubin/Albumin Ratio with Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Jan 24;16:273-280. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S393273. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 36718146 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between bilirubin and systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Dec;11(12):e1115. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1115. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 38156396 Free PMC article.
-
The role of bilirubin as a biomarker of rheumatic diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 14;15:1369284. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1369284. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38947324 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Chinese visceral adiposity index increases the risk of stroke in Chinese patients with metabolic syndrome.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 29;14:1218905. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1218905. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37455909 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

