Study of Hearing Status in COVID-19 Patients: A Multicentered Review
- PMID: 34277385
- PMCID: PMC8274964
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-021-02710-w
Study of Hearing Status in COVID-19 Patients: A Multicentered Review
Abstract
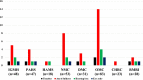
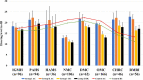
To evaluate the hearing status of COVID-19 patients and compare with control group. Prospective study carried out in 9 institutes. The pure tone audiogram and impedance audiometry of COVID-19 patients performed initially and at 3 months follow up. The control group consisted COVID-19 negative individuals with no history of ear related diseases. The average of air and bone conduction threshold (AC and BC) were compared between the COVID-19 patients and control group using independent t-test with a p value of less than 0.05 considered significant. Total of 331 patients, age 32 ± 4.3 years, 66.7% males and 33.3% females were included in the study. There were 80 individuals in the control group. Aural symptoms were, tinnitus in 1.8%, aural fullness in 1.4%, hearing loss in 3. 9%, and ear ache in 1.8% were present initially, resolved at 3 months follow up. The impedance audiometry demonstrated type B and type C curve in 5.1% and 1.15% ears, and out of these 64.7% and 40% improved at 3 months follow up respectively. No significant difference observed between the average AC and BC of the COVID-19 patients and control group. The COVID-19 infection may present with aural symptoms; however, it was concluded that there was no significant difference in the hearing status of the COVID-19 positive patients in comparison to the control group. The presence of some changes in the normal functioning of the eustachian tube and middle ear in the COVID-19 infection was also highlighted.
Keywords: COVID-19; Hearing; Impedance audiometry; Pure tone audiometry.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
