Preliminary Assessment of Chinese Strategy in Controlling Reemergent Local Outbreak of COVID-19
- PMID: 34277536
- PMCID: PMC8283522
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.650672
Preliminary Assessment of Chinese Strategy in Controlling Reemergent Local Outbreak of COVID-19
Abstract
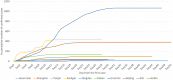
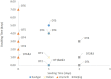
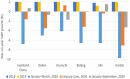
Reemergent local outbreaks of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) have occurred in China, yet few Chinese response strategies and its evaluation have been reported. This study presents a preliminary assessment of Chinese strategy in controlling reemergent local outbreaks of COVID-19. Time course of accumulative and daily new cases and time-varying reproductive numbers (Rt) of outbreak areas were presented. The asymptomatic rate, days required to control the outbreaks, seeding time (ST), and doubling time (DT) of areas with over 96 reemergent cases were calculated. National and local year-on-year growth rates of gross domestic product (GDP) were presented. Accumulative numbers of 30, 8, 11, 430, 15, 139, 1,067, 382, 42, and 94 confirmed reemergent COVID-19 cases were diagnosed in Hulun Buir, Shanghai, Tianjin, Kashgar, Qingdao, Dalian, Urumchi, Beijing, Jilin, and Harbin, respectively. Among them, maximum rate of asymptomatic infections was 81.9%. Time required to control the local outbreaks in the areas given above varied from 29 to 51 days. After activation of outbreak responses, the late-stage DTs of Kashgar, Urumchi, Beijing, and Dalian were apparently lengthened compared to the early-stage DTs. Although the year-on-year GDP growth rate of Urumchi was slightly affected, the GDP growth rate of Dalian, Beijing, Jilin, and Harbin kept rising during the reemergence. Moreover, the year-on-year GDP growth rate of Mainland China turned positive regardless of the reemergent local outbreaks. In general, the Chinese strategy to maintain the status of no or minimal transmission was effective in balancing the control of COVID-19 reemergent local outbreak and the recovery of economy.
Keywords: COVID-19; China; GDP; SARS-CoV-2; asymptomatic infection; reemergent local outbreak.
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Jin, Jin, Lu, Yu, Li and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
COVID-19 epidemic phases and morbidity in different areas of Chinese mainland, 2020.Front Public Health. 2023 Apr 6;11:1151038. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1151038. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37089485 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological clustered characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in three phases of transmission in Jilin Province, China.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 19;18(1):e0279879. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279879. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36656818 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of epidemiological characteristics and transmissibility of different strains of COVID-19 based on the incidence data of all local outbreaks in China as of March 1, 2022.Front Public Health. 2022 Sep 15;10:949594. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.949594. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36187650 Free PMC article.
-
Universal screening for SARS-CoV-2 infection: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 15;9(9):CD013718. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013718. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33502003 Free PMC article.
-
The First 75 Days of Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Outbreak: Recent Advances, Prevention, and Treatment.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Mar 30;17(7):2323. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17072323. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32235575 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Complex Contact Network of Patients at the Beginning of an Epidemic Outbreak: An Analysis Based on 1218 COVID-19 Cases in China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jan 8;19(2):689. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19020689. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35055511 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling the pulse population-wide nucleic acid screening in mitigating and stopping COVID-19 outbreaks in China.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 May 3;23(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08265-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37138230 Free PMC article.
-
Using search trends to analyze web-based users' behavior profiles connected with COVID-19 in mainland China: infodemiology study based on hot words and Baidu Index.PeerJ. 2022 Nov 9;10:e14343. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14343. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36389414 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of clinical indications and viral strain variants among patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Inner Mongolia, China.Virus Genes. 2023 Jun;59(3):391-398. doi: 10.1007/s11262-023-01986-0. Epub 2023 Mar 11. Virus Genes. 2023. PMID: 36905534 Free PMC article.
-
Point-of-care CRISPR/Cas biosensing technology: A promising tool for preventing the possible COVID-19 resurgence caused by contaminated cold-chain food and packaging.Food Front. 2022 Oct 12:10.1002/fft2.176. doi: 10.1002/fft2.176. Online ahead of print. Food Front. 2022. PMID: 36712576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. WHO (2020). Available online at: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed December 30, 2020).
-
- Department of Communications WHO Headquarters . COVID-19 Virtual Press Conference Transcript−16 November 2020. Department of Communications WHO Headquarters (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-virtual-press-conferenc... (accessed November 22, 2020).
-
- Beijing Municipal Health Commission . Situation updates of COVID-19 in Beijing. Beijing Municipal Health Commission (2020). Available online at: http://wjw.beijing.gov.cn/wjwh/ztzl/xxgzbd/gzbdyqtb/ (accessed November 19, 2020).
-
- Health Commission of Dalian . Situation updates of COVID-19 in Dalian. Health Commission of Dalian (2020). Available https://www.dl.gov.cn/col/col459/index.html (accessed December 2, 2020).
-
- Heilongjiang Municipal Health Commission . Situation updates of COVID-19 in Heilongjiang. Heilongjiang Municipal Health Commission (2020). Available online at: http://wsjkw.hlj.gov.cn/pages/5df84bfaf6e9fa23e8848a48 (accessed December 9, 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

