Is Fatty Liver Associated With Depression? A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review on the Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Depression and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- PMID: 34277666
- PMCID: PMC8278401
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.691696
Is Fatty Liver Associated With Depression? A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review on the Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Depression and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
Background and Aims: Both non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and depression have a high global prevalence which is projected to increase further. While studies exploring the association have been done, there are conflicting data. This study aims to assess the prevalence and association between depression and NAFLD. Methods: Medline and Embase were searched from inception to March 3, 2020. Meta-analysis of proportions using the generalized linear mix model was conducted to analyze the pooled prevalence of depression in NAFLD patients. Risk factors for depression in NAFLD patients were evaluated in conventional pairwise meta-analysis. Results: Ten studies involving 2,041,752 NAFLD patients were included. Pooled prevalence of depression was 18.21% (CI: 11.12-28.38%) in patients with NAFLD and 40.68% (CI: 25.11-58.37%) in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). NAFLD resulted in significantly higher risk of development of depression (OR: 1.29, CI: 1.02-1.64, p = 0.03). NASH patients had a significantly higher risk of depression compared with NAFLD patients (RR: 2.83, CI: 2.41-3.32, p < 0.001). Diabetes, body mass index (BMI), female sex, smoking, and history of pulmonary disease were significant risk factors for depression in NAFLD patients. Conclusion: This study demonstrated a high prevalence of depression in NAFLD patients and a significant association between both conditions. Furthermore, patients with NASH had a significantly higher risk of depression compared with those with NAFLD. Diabetes, BMI, history of lung disease or smoking, and female gender were significant risk factors. Further studies investigating the pathophysiological mechanism underlying depression and NAFLD are needed.
Keywords: evidence-based practice; fatty liver; mental health; metabolic disease; mood disorder.
Copyright © 2021 Xiao, Lim, Ng, Tan, Lim, Ho, Tan, Sanyal and Muthiah.
Conflict of interest statement
AS: President of Sanyal Biotechnology and has stock options in Genfit, Akarna, Tiziana, Indalo, Durect and Galmed. He has served as a consultant to Astra Zeneca, Nitto Denko, Enyo, Ardelyx, Conatus, Nimbus, Amarin, Salix, Tobira, Takeda, Jannsen, Gilead, Terns, Birdrock, Merck, Valeant, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Lilly, Hemoshear, Zafgen, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Exhalenz and Genfit. He has been an unpaid consultant to Intercept, Echosens, Immuron, Galectin, Fractyl, Syntlogic, Affimune, Chemomab, Zydus, Nordic Bioscience, Albireo, Prosciento, Surrozen and Bristol Myers Squibb. His institution has received grant support from Gilead, Salix, Tobira, Bristol Myers, Shire, Intercept, Merck, Astra Zeneca, Malinckrodt, Cumberland and Novartis. He receives royalties from Elsevier and UptoDate. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
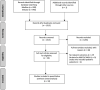
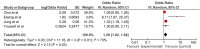


Similar articles
-
The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Hepatol. 2019 Oct;71(4):793-801. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.021. Epub 2019 Jul 4. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31279902
-
An Observational Data Meta-analysis on the Differences in Prevalence and Risk Factors Between MAFLD vs NAFLD.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Mar;21(3):619-629.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.11.038. Epub 2021 Dec 4. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 34871813 Review.
-
Prevalence of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in India: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022 May-Jun;12(3):818-829. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2021.11.010. Epub 2021 Nov 25. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35677499 Free PMC article.
-
High parathyroid hormone level as a marker of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2023 Aug;17(8):102827. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2023.102827. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2023. PMID: 37451113
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and coexisting depression, anxiety and/or stress in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 16;15:1357664. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1357664. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38689730 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association between smoking and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Southeast Asia.Front Public Health. 2022 Dec 13;10:1008878. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1008878. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36582387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Foregut bypass vs. restrictive bariatric procedures for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis of 3,355 individuals.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2023 Oct 1;12(5):658-670. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-21-520. Epub 2022 Jun 20. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37886204 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Community series - liver fibrosis and MAFLD: from molecular aspects to novel pharmacological strategies, volume II.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 2;11:1371720. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1371720. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38371514 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Prevalence of depression and anxiety symptoms by liver disease etiology.Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2023 Jul 11;22(3):89-94. doi: 10.1097/CLD.0000000000000068. eCollection 2023 Sep. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2023. PMID: 37799635 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Differential Expression of Lipid Metabolism Genes, CROT and ABCG1, in Obese Patients with Comorbid Depressive Disorder and Risk of MASLD.Metabolites. 2025 Jun 11;15(6):392. doi: 10.3390/metabo15060392. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 40559416 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

