Network Pharmacology-Based Dissection of the Active Ingredients and Protective Mechanism of the Salvia Miltiorrhiza and Panax Notoginseng Herb Pair against Insulin Resistance
- PMID: 34278114
- PMCID: PMC8280704
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c01209
Network Pharmacology-Based Dissection of the Active Ingredients and Protective Mechanism of the Salvia Miltiorrhiza and Panax Notoginseng Herb Pair against Insulin Resistance
Abstract
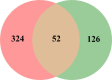
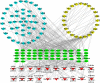
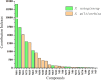
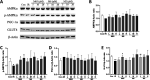
The Salvia miltiorrhiza and Panax notoginseng herb pair (DQ) has been widely utilized in traditional Chinese medicine for the longevity and for preventing and treating cardio-cerebrovascular diseases. Often associated with cardio-cerebrovascular diseases are comorbidities such as insulin resistance. However, the protective mechanisms of DQ against insulin resistance remain not well understood. Through network pharmacology analysis, a total of 94 candidate active compounds selected from DQ (61 from S. miltiorrhiza Bunge and 33 from P. notoginseng (Burk.) F. H. Chen) interacted with 52 corresponding insulin resistance-related targets, which mainly involved insulin resistance and the AMPK signaling pathway. Furthermore, the contribution index calculation results indicated 25 compounds as the principal components of this herb pair against insulin resistance. Among them, ginsenoside F2, protocatechuic acid, and salvianolic acid B were selected and validated to promote glucose consumption through activating AMPK phosphorylation and upregulating GLUT4 in insulin-resistant cell model (HepG2/IR) cells. These findings indicated that DQ has the potential for repositioning in the treatment of insulin resistance mainly through the AMPK signaling pathway.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of serum lipidomics and amino acid profiles of rats with acute myocardial ischemia by Salvia miltiorrhiza and Panax notoginseng herb pair.Phytomedicine. 2020 Feb;67:153162. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153162. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 31955134
-
Effective Components of Panax notoginseng-Salvia miltiorrhiza in the Treatment of Melasma and Its Experimental Study.ACS Omega. 2025 Jan 14;10(3):3033-3043. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c09799. eCollection 2025 Jan 28. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39895736 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Jul 21;188:234-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.005. Epub 2016 May 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27154405 Review.
-
In vivo distribution and pharmacokinetics of multiple active components from Danshen and Sanqi and their combination via inner ear administration.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Oct 28;156:199-208. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.08.041. Epub 2014 Sep 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25218322
-
Panax Notoginseng Saponins: A Review of Its Mechanisms of Antidepressant or Anxiolytic Effects and Network Analysis on Phytochemistry and Pharmacology.Molecules. 2018 Apr 17;23(4):940. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040940. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29673237 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the effective compounds and potential mechanisms of Shengxian Decoction against coronary heart disease by UPLC-Q-TOF/MS and network pharmacology analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 16;10(8):e29558. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29558. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38681620 Free PMC article.
-
From waste to wonder: exploring the hypoglycemic and anti-oxidant properties of corn processing by-products.Front Chem. 2024 Jul 18;12:1433501. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1433501. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 39104778 Free PMC article.
-
Methodology of network pharmacology for research on Chinese herbal medicine against COVID-19: A review.J Integr Med. 2022 Nov;20(6):477-487. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2022.09.004. Epub 2022 Sep 22. J Integr Med. 2022. PMID: 36182651 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xiong X. J.; Wang Z.; Wang J. Innovative strategy in treating angina pectoris with Chinese patent medicines by promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis: experience from combination therapy in Chinese medicine. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 13, 540–553. 10.2174/1570161112666141014153735. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baek E. B.; Yoo H. Y.; Park S. J.; Chung Y. S.; Hong E. K.; Kim S. J. Inhibition of arterial myogenic responses by a mixed aqueous extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza and Panax notoginseng (PASEL) showing antihypertensive effects. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 13, 287–293. 10.4196/kjpp.2009.13.4.287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

