A Completely Endovascular Solution for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Embolisation and Inversion into the Aortic Arch
- PMID: 34278368
- PMCID: PMC8264528
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejvsvf.2021.06.003
A Completely Endovascular Solution for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Embolisation and Inversion into the Aortic Arch
Abstract
Introduction: Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) has evolved into the preferred alternative to surgical valve replacement for severe aortic valve stenosis with high surgical risk. With expanding indications, life threatening complications including transcatheter aortic valve embolisation and inversion (TAVEI), in which the valve dislodges, inverts, and migrates caudally, may increase concomitantly.
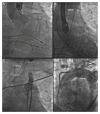
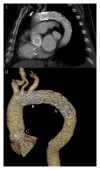
Report: An 80 year old male with severe aortic valve stenosis underwent balloon expandable transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI). Valve embolisation into the aortic arch inverted the bioprothesis, excluding the option of fixation in the descending aorta. Through-valve thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR) was performed after bifemoral snaring using a through-and-through wire technique and pulling the valve into the descending aorta.
Discussion: TAVI is emerging as the preferred treatment for severe aortic valve stenosis and comes with unique procedural complications, such as life threatening transcatheter aortic valve embolisation and inversion (TAVEI). Although some authors prefer treating embolisation of a non-inverted balloon expandable valve into the aorta by using the valvuloplasty balloon to pull the valve distally and fixing it in the descending aorta, this risks further expansion of the valve and consequently fixing it in an undesirable position and is not possible if the valve inverts. Downstream placement of the valve by snaring with a guiding catheter covering/protecting a through-and-through wire technique, combined with through-valve TEVAR, provides a new bail out strategy for this serious complication and may reduce TAVEI associated mortality and morbidity.
Keywords: Aortic (valve) stenosis; Embolisation; Endovascular; TAVI; Thoracic stent graft.
© 2021 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Mack M.J., Leon M.B., Thourani V.H., Makkar R., Kodali S.K., Russo M. Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement with a balloon-expandable valve in low-risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1695–1705. - PubMed
-
- Thourani V.H., Kodali S., Makkar R.R., Herrmann H.C., Williams M., Babaliaros V. Transcatheter aortic valve replacement versus surgical valve replacement in intermediate-risk patients: a propensity score analysis. Lancet. 2016;387:2218–2225. - PubMed
-
- Ibebuogu U.N., Giri S., Bolorunduro O., Tartara P., Kar S., Holmes D. Review of reported causes of device embolization following trans-catheter aortic valve implantation. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115:1767–1772. - PubMed
-
- Ali A., Altwegg L., Horlick E., Feindel C., Thompson C., Cheung A. Prevention and management of transcatheter balloon-expandable aortic valve malposition. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2008;72:573–578. - PubMed
-
- Stern J.R., Cafasso D.E., Schneider D.B., Meltzer A.J. Totally Percutaneous Fenestration via the “Cheese-wire” technique to facilitate endovascular aneurysm repair in chronic aortic dissection. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2018;52:218–221. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
