Double-jeopardy: scRNA-seq doublet/multiplet detection using multi-omic profiling
- PMID: 34278374
- PMCID: PMC8262260
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2021.100008
Double-jeopardy: scRNA-seq doublet/multiplet detection using multi-omic profiling
Abstract
The computational detection and exclusion of cellular doublets and/or multiplets is a cornerstone for the identification the true biological signals from single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data. Current methods do not sensitively identify both heterotypic and homotypic doublets and/or multiplets. Here, we describe a machine learning approach for doublet/multiplet detection utilizing VDJ-seq and/or CITE-seq data to predict their presence based on transcriptional features associated with identified hybrid droplets. This approach highlights the utility of leveraging multi-omic single-cell information for the generation of high-quality datasets. Our method has high sensitivity and specificity in inflammatory-cell-dominant scRNA-seq samples, thus presenting a powerful approach to ensuring high-quality scRNA-seq data.
Keywords: ADT; B cell receptor; CITE-seq; T cell receptor; doublets; multi-omics profiling; single-cell transcriptomics.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
R.J.M.B.-R. is a co-founder of Alchemab Therapeutics Ltd and consultant for Alchemab Therapeutics Ltd and GSK. F.A.T. is a consultant for Alchemab Therapeutics Ltd.
Figures

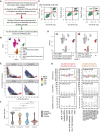
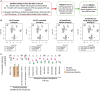


References
-
- Barreto V., Cumano A. Frequency and characterization of phenotypic Ig heavy chain allelically included IgM-expressing B cells in mice. J. Immunol. 2000;164:893–899. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

