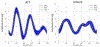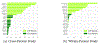Detection of Junctional Ectopic Tachycardia by Central Venous Pressure
- PMID: 34278383
- PMCID: PMC8281976
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-77211-6_29
Detection of Junctional Ectopic Tachycardia by Central Venous Pressure
Abstract
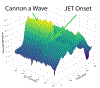
Central venous pressure (CVP) is the blood pressure in the venae cavae, near the right atrium of the heart. This signal waveform is commonly collected in clinical settings, and yet there has been limited discussion of using this data for detecting arrhythmia and other cardiac events. In this paper, we develop a signal processing and feature engineering pipeline for CVP waveform analysis. Through a case study on pediatric junctional ectopic tachycardia (JET), we show that our extracted CVP features reliably detect JET with comparable results to the more commonly used electrocardiogram (ECG) features. This machine learning pipeline can thus improve the clinical diagnosis and ICU monitoring of arrhythmia. It also corroborates and complements the ECG-based diagnosis, especially when the ECG measurements are unavailable or corrupted.
Keywords: Automatic Arrythmia Detection; Central Venous Pressure; Junctional Ectopic Tachycardia; Physiological Signal Feature Extraction.
Figures
References
-
- Central venous pressure - evaluation, interpretation, monitoring, clinical implications. Bratisl Lek Listy 109(4), 185–187 - PubMed
-
- Segmentation of heart sound recordings by a duration-dependent hidden markov model. Physiological Measurement 31(4), 513–529 (2011) - PubMed
-
- Data and statistics on congenital heart defects — cdc (November 2018), https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/heartdefects/data.html
-
- Bigatello LM, George E: Hemodynamic monitoring. Minerva Anestesiologica 68(4), 219–225 (April 2002), https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12024086/ - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources