Interactions between the ERK1/2 signaling pathway and PCAF play a key role in PE‑induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
- PMID: 34278478
- PMCID: PMC8281443
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12275
Interactions between the ERK1/2 signaling pathway and PCAF play a key role in PE‑induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
Abstract
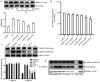
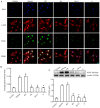
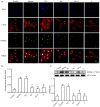
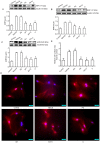
Cardiomyocyte hypertrophy is a compensatory phase of chronic heart failure that is induced by the activation of multiple signaling pathways. The extracellular signal‑regulated protein kinase (ERK) signaling pathway is an important regulator of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. In our previous study, it was demonstrated that phenylephrine (PE)‑induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy involves the hyperacetylation of histone H3K9ac by P300/CBP‑associated factor (PCAF). However, the upstream signaling pathway has yet to be fully identified. In the present study, the role of the extracellular signal‑regulated protein kinase (ERK)1/2 signaling pathway in PE‑induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy was investigated. The mice cardiomyocyte hypertrophy model was successfully established by treating cells with PE in vitro. The results showed that phospho‑(p‑)ERK1/2 interacted with PCAF and modified the pattern of histone H3K9ac acetylation. An ERK inhibitor (U0126) and/or a histone acetylase inhibitor (anacardic acid; AA) attenuated the overexpression of phospho‑ERK1/2 and H3K9ac hyperacetylation by inhibiting the expression of PCAF in PE‑induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Moreover, U0126 and/or AA could attenuate the overexpression of several biomarker genes related to cardiac hypertrophy (myocyte enhancer factor 2C, atrial natriuretic peptide, brain natriuretic peptide and β‑myosin heavy chain) and prevented cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. These results revealed a novel mechanism in that AA protects against PE‑induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in mice via the ERK1/2 signaling pathway, and by modifying the acetylation of H3K9ac. These findings may assist in the development of novel methods for preventing and treating hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: ERK‑signaling pathway; anacardic acid; cardiomyocyte hypertrophy; histone acetylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Degoricija V, Trbušić M, Potočnjak I, Radulović B, Terešak SD, Pregartner G, Berghold A, Tiran B, Frank S. Acute heart failure developed as worsening of chronic heart failure is associated with increased mortality compared to de novo cases. Sci Rep. 2018;8:9587. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28027-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

