Informant Questionnaire on Cognitive Decline in the Elderly (IQCODE) for the detection of dementia within community dwelling populations
- PMID: 34278562
- PMCID: PMC8407460
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010079.pub3
Informant Questionnaire on Cognitive Decline in the Elderly (IQCODE) for the detection of dementia within community dwelling populations
Abstract
Background: Various tools exist for initial assessment of possible dementia with no consensus on the optimal assessment method. Instruments that use collateral sources to assess change in cognitive function over time may have particular utility. The most commonly used informant dementia assessment is the Informant Questionnaire on Cognitive Decline in the Elderly (IQCODE). A synthesis of the available data regarding IQCODE accuracy will help inform cognitive assessment strategies for clinical practice, research and policy.
Objectives: Our primary obective was to determine the accuracy of the informant-based questionnaire IQCODE for detection of dementia within community dwelling populations. Our secondary objective was to describe the effect of heterogeneity on the summary estimates. We were particularly interested in the traditional 26-item scale versus the 16-item short form; and language of administration. We explored the effect of varying the threshold IQCODE score used to define 'test positivity'.
Search methods: We searched the following sources on 28 January 2013: ALOIS (Cochrane Dementia and Cognitive Improvement Group), MEDLINE (OvidSP), EMBASE (OvidSP), PsycINFO (OvidSP), BIOSIS Previews (ISI Web of Knowledge), Web of Science with Conference Proceedings (ISI Web of Knowledge), LILACS (BIREME). We also searched sources relevant or specific to diagnostic test accuracy: MEDION (Universities of Maastrict and Leuven); DARE (York University); ARIF (Birmingham University). We used sensitive search terms based on MeSH terms and other controlled vocabulary.
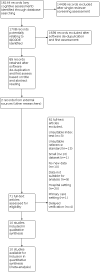
Selection criteria: We selected those studies performed in community settings that used (not necessarily exclusively) the IQCODE to assess for presence of dementia and, where dementia diagnosis was confirmed with clinical assessment. Our intention with limiting the search to a 'community' setting was to include those studies closest to population level assessment. Within our predefined community inclusion criteria, there were relevant papers that fulfilled our definition of community dwelling but represented a selected population, for example stroke survivors. We included these studies but performed sensitivity analyses to assess the effects of these less representative populations on the summary results.
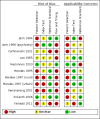
Data collection and analysis: We screened all titles generated by the electronic database searches and abstracts of all potentially relevant studies were reviewed. Full papers were assessed for eligibility and data extracted by two independent assessors. For quality assessment (risk of bias and applicability) we used the QUADAS 2 tool. We included test accuracy data on the IQCODE used at predefined diagnostic thresholds. Where data allowed, we performed meta-analyses to calculate summary values of sensitivity and specificity with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs). We pre-specified analyses to describe the effect of IQCODE format (traditional or short form) and language of administration for the IQCODE.
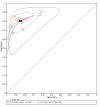
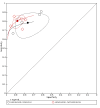
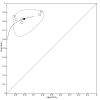
Main results: From 16,144 citations, 71 papers described IQCODE test accuracy. We included 10 papers (11 independent datasets) representing data from 2644 individuals (n = 379 (14%) with dementia). Using IQCODE cut-offs commonly employed in clinical practice (3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6) the sensitivity and specificity of IQCODE for diagnosis of dementia across the studies were generally above 75%. Taking an IQCODE threshold of 3.3 (or closest available) the sensitivity was 0.80 (95% CI 0.75 to 0.85); specificity was 0.84 (95% CI 0.78 to 0.90); positive likelihood ratio was 5.2 (95% CI 3.7 to 7.5) and the negative likelihood ratio was 0.23 (95% CI 0.19 to 0.29). Comparative analysis suggested no significant difference in the test accuracy of the 16 and 26-item IQCODE tests and no significant difference in test accuracy by language of administration. There was little difference in sensitivity across our predefined diagnostic cut-points. There was substantial heterogeneity in the included studies. Sensitivity analyses removing potentially unrepresentative populations in these studies made little difference to the pooled data estimates. The majority of included papers had potential for bias, particularly around participant selection and sampling. The quality of reporting was suboptimal particularly regarding timing of assessments and descriptors of reproducibility and inter-observer variability.
Authors' conclusions: Published data suggest that if using the IQCODE for community dwelling older adults, the 16 item IQCODE may be preferable to the traditional scale due to lesser test burden and no obvious difference in accuracy. Although IQCODE test accuracy is in a range that many would consider 'reasonable', in the context of community or population settings the use of the IQCODE alone would result in substantial misdiagnosis and false reassurance. Across the included studies there were issues with heterogeneity, several potential biases and suboptimal reporting quality.
Copyright © 2021 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The review authors have no declarations specific to the review.
Figures





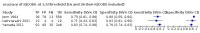

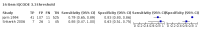
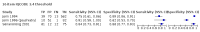
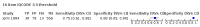
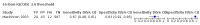
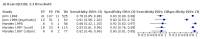
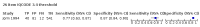
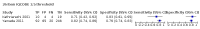
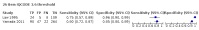

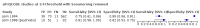
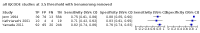
Update of
-
Informant Questionnaire on Cognitive Decline in the Elderly (IQCODE) for the diagnosis of dementia within community dwelling populations.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 10;(4):CD010079. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010079.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jul 19;7:CD010079. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010079.pub3. PMID: 24719028 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Jorm 1994 {published data only}
-
- Jorm AF. A short form of the Informant Questionnaire on Cognitive Decline in the Elderly (IQCODE): development and cross validation. Psychological Medicine 1994;24:145-53. - PubMed
Jorm 1996 (psychiatry) {published data only}
-
- Jorm AF, Christensen H, Henderson AS, Jacomb PA, Korten AE, Mackinnon A. Informant ratings of cognitive decline of elderly people relationship to longitudinal change on cognitive tests. Age and Ageing 1996;25:125-9. - PubMed
Kathriarachi 2001 {published and unpublished data}
Law 1995 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Law S, Wolfson C. Validation of a French version of an informant based questionnaire as a screening test for Alzheimer's disease. British Journal of Psychiatry 1995;167:541-4. - PubMed
Mackinnon 2003 {published data only}
-
- Mackinnon A, Khalilian A, Jorm AF, Korten AE, Christensen H, Mulligan R. Improving screening accuracy for dementia in a community sample by augmenting cognitive testing with informant report. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2003;56:358–66. - PubMed
Morales 1995 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Morales JM, Gonzalez-Montalvo JI, Bermejo F, Del-Ser T. The screening of mild dementia with a shortened Spanish version of the Informant Questionnaire on Cognitive Decline in the Elderly. Alzheimer's Disease and Associated Disorders 1995;9:105-11. - PubMed
Morales 1997 (rural) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Morales JM, Bermejo F, Romero M, Del-Ser T. Screening of dementia in community dwelling elderly through informant report. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1997;12:808-16. [these are data from independent rural cohort] - PubMed
Morales 1997 (urban) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Morales JM, Bermejo F, Romero M, Del-Ser T. Screening of dementia in community dwelling elderly through informant report. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1997;12:808-16. - PubMed
Senanorong 2001 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Senanarong V, Assavisaraporn S, Sivasiriyanonds N, Printarakul T, Jamjumrus S, Udompunthurunk S, Poungvarin N. The IQCODE an alternative screening test for dementia for low educated Thai elderly. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 2001;84:648-55. - PubMed
Srikanth 2006 {published data only}
-
- Srikanth V, Thrift AG, Fryer JL, Saling MM. The validity of brief screening cognitive assessments in the diagnosis of cognitive impairments and dementia after first ever stroke. International Psychogeriatrics 2006;18:295-305. - PubMed
Yamada 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Mimori Y, Miyachi T, Ohshita T, Nakamura S, Yamada M, Sasaki H, Suzuki G. Cognitive decline and detection of dementia among the Japanese population. Anlaysis with the CASI and IQCODE. In: conference proceedings (poster). 2011.
References to studies excluded from this review
Abreu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Abreu ID, Nunes PV, Diniz BS, Forlenza OV. Combining functional scales and cognitive tests in screening for mild cognitive impairment at a university based memory clinic in Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Pisquiatria 2008;30:346-9. - PubMed
Butt 2008 {published data only}
-
- Butt Z. Sensitivity of the IQCODE an application of item response theory. Aging, Neuropsychology and Cognition 2008;15:642-55. - PubMed
Cherbuin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Cherbuin N, Anstey KJ, Lipnicki DM. Screening for dementia a review of self and informant assessment instruments. International Psychogeriatrics 2008;20:431-58. - PubMed
de Jonge 1997 {published data only}
-
- De Jonghe JFM. Differentiating between demented and psychiatric patients with the dutch version of IQCODE. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1997;12:462-5. - PubMed
Dekkers 2009 {published data only}
-
- Dekkers M, Joosten-Weyn Banningh EW, Eling PA. Awareness in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Tijdschrift voor Gerontologie en Geriatrie 2009;40:17-23. - PubMed
Diefeldt 2007b {published data only}
-
- Diesfeldt HFA. Informant based measures may over estimate cognitive impairment in elderly patients. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2007;22:1166-70. - PubMed
Diesfeldt 2007 {published data only}
-
- Diesfeldt HFA. Discrepancies between IQCODE and cognitive test performance. Tijdschrift voor Gerontologie en Geriatrie 2007;38:199-209. - PubMed
Ehrensperger 2010 {published data only}
-
- Enrensperger MM, Berres M, Taylor KI, Monsch AU. Screening properties of the German IQCODE with a two year time frame in MCI and early Alzheimer's disease. International Psychogeriatrics 2010;22:91-100. - PubMed
Farias 2002 {published data only}
Finneli (abstract) {published data only}
-
- Finelli L, Kunze U, Gautier A, Gomez-Mancilla B, Monsch AU. Algorithms to retrospectively diagnose mild cognitive impairment and dementia in a longitudinal study of ageing and dementia. In: abstract ICAD. 2009.
Fuh 1995 {published data only}
-
- Fuh JL, Teng EL, Lin KN, Larson EB, Wang SJ, Liu CY et al. The Informant Questionnaire on Cognitive Dcline in the Elderly as a screening tool for dementia for a predominantly illiterate Chinese population. Neurology 1995;45:92-6. - PubMed
Garcia 2002 {published data only}
-
- Forcano Garcia M, Perlado Ortiz de Pinedo F. Cognitive deterioration: use of the short version of the Informant Test (IQCODE) in the geriatrics consultations. Revista Espanola de Geriatria y Gerontolgia 2002;37:81-5.
Goncalves 2011 {published data only}
-
- Goncalves DC, Arnold E, Appadurai K, Byrne GJ. Case finding in dementia: comparative utility of three brief instruments in the memory clinic setting. International Psychogeriatrics 2011;23:788-96. - PubMed
Hancock 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hancock P, Larner AJ. Diagnostic utility of the IQCODE and its combination with ACE-R in a memory clinic based population. International Psychogeriatrics 2009;21:526-30. - PubMed
Harwood 1997 {published data only}
-
- Harwood DMJ, Hope T, Jacoby R. Cognitive impairment in medical inpatients - screening for dementia is history better than mental state. Age and Ageing 1997;26:31-5. - PubMed
Hayden 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hayden KM, Khachaturian AS, Tschanz JT, Corcoran C, Nortond M, Breitner JCS. Characteristics of a two-stage screen for incident dementia. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2003;56:1038-45. - PubMed
Henon 2001 {published data only}
-
- Henon H, Durieu I, Guerouaou D, Lebert F, Pasquier F, Leys D. Poststroke dementia incidence and relationship to pre-stroke cognitive decline. Neurology 2001;57:1216-22. - PubMed
Isella 2002 {published data only}
-
- Isella V, Villa ML, Frattola L, Appollonio I. Screening cognitive decline in dementia preliminary data on the Italian version of the IQCODE. Neurological Sciences 2002;23:s79-s80. - PubMed
Isella 2006 {published data only}
Jorm 1989 {published data only}
-
- Jjorm AF, Scott R, Jacomb PA. Assessment of cognitive decline in dementia by informant questionnaire. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1989;4:35-9.
Jorm 1989b {published data only}
-
- Jorm AF, Jacomb PA. The IQCODE; sociodemographic correlates, reliability, validity and some norms. Psychological Medicine 1989;19:1015-22. - PubMed
Jorm 1991 {published data only}
-
- Jorm AF, Scott R, Cullen JS, MacKinnon AJ. Performance of the IQCODE as a screening test for dementia. Psychological Medicine 1991;21:785-90. - PubMed
Jorm 1996 (Age and Ageing {published data only}
-
- Jorm AF, Christensen H, Henderson AS, Jacomb PA, Korten AE, Mackinnon A. Informant ratings of cognitive decline of elderly people relationships to longitudinal change on cognitive tests. Age and Ageing 1996;25:125-9. - PubMed
Jorm 1997 {published data only}
-
- Jorm AF. Methods of screening for dementia: a meta-analysis of studies comparing an informant interview with a brief cognitive test. Alzheimers Disease and Associated Disorders 1997;11:158-62. - PubMed
Jorm 2000 {published data only}
-
- Jorm AF, Christensen H, Korten AE, Jacomb PA, Henderson AS. Informant ratings of cognitive decline in old age. Psychological Medicine 2000;30:981-5. - PubMed
Jorm 2003 {published data only}
-
- Jorm AF. The value of informant reports for assessment and prediction of dementia. Journal of the American Geriatrics Association 2003;51:881-2. - PubMed
Jorm 2004 {published data only}
-
- Jorm AF. The IQCODE: a review. International Psychogeriatrics 2004;16:275-93. - PubMed
Khachaturian 2000 {published data only}
-
- Khachaturian AS, Gallo JJ, Breitner JC. Performance characteristics of a two stage dementia screen in a population sample. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2000;53:531-40. - PubMed
Knaefelc 2003 {published data only}
-
- Knafelc R, Giudice DL, Harrigan S, Cook R, Flicker L, Mackinnon A, Ames D. The combination of cognitive testing and an informant questionnaire in screening for dementia. Age and Ageing 2003;32:541-547. - PubMed
Krogseth 2011 {published data only}
-
- Krogseth M, Wyller TB, Engedal K, Juliebo V. Delirium is an important predictor of incident dementia among elderly hip fracture patients. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2011;31:63-70. - PubMed
Larner 2010 {published data only}
-
- Larner AJ. Can IQCODE differentiate Alzheimer's disease from frontotemporal dementia. Age and Ageing 2010;39:392-4. - PubMed
Larner 2013 {published data only}
-
- Cherbuin N, Jorm AF. Chapter 8. The Informant Questionnaire for Cognitive Decline in the Elderly. In: Larner AJ, editors(s). Cognitive Screening Instruments. London: Springer-Verlag, 2013:166-79.
Li 2012 {published data only}
-
- Li F, Jia XF, Jia J. The Informant Questionnaire on Cognitive Decline in the Elderly individuals in screening mild cognitive impairment with or without functional impairment. Journal Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology 2012;25:227-32. - PubMed
Louis 1999 {published data only}
-
- Louis B, Harwood D, Hope T, Jacoby R. Can an informant questionnaire be used to predict the development of dementia in medical inpatients. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1999;14:941-5. - PubMed
Mackinnon 1998 {published data only}
-
- Mackinnon A, Mulligan R. Combining cognitive testing and informant report to increase accuracy in screening for dementia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1998;155:1529-35. - PubMed
Mimori (abstract) {published data only}
-
- Mimori Y. Cognitive decline and detection of dementia among the Japanese population analysis with CASI and IQCODE. In: abstract. 2010:s451.
Morales‐Gonzalez 1992 {published data only}
-
- Morales-Gonzalez JM, Gonzalez-Montalvo JL, De Ser Quijano T, Bermejo Pareja F. Validation of the S-IQCODE [Original paper in Spanish]. Archivos de Neurobiologiá (Madrid) 1992;55:262-6. - PubMed
Mulligan 1996 {published data only}
-
- Mulligan R, Mackinnon A, Jorm A, Giannakopoulos P, Michel J. A comparison of alternative methods of screening for dementia in clinical settings. Archives of Neurology 1996;53:532-6. - PubMed
Narasimhalu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Narasimhalu K, Lee J, Auchus AP, Chen CPLH. Improving detection of dementia in Asian patients with low education combining the MMSE and the IQCODE. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2008;25:17-22. - PubMed
Ozel‐kizel 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ozel-Kizel ET, Turan ED, Yilmaz E, Cangoz B, Uluc S. Discriminant validity and reliability of the Turkish version of the IQCODE. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 2010;25:139-45. - PubMed
Peroco 2009 {published data only}
-
- Perroco TR, Zevallos Bustamente SE, Pilar Q, Moreno M, Hototian SR, Lopes MA et al. Performance of Brazilian long and short IQCODE on the screening of dementia in elderly people with low education. International Psychogeriatrics 2009;21:531-8. - PubMed
Potter 2009 {published data only}
Razavi 2011 {published and unpublished data}
Ritchie 1992 {published data only}
-
- Ritchie K, Fuhrer R. A comparative study of the performance of screening tests for senile dementia using receiver operating characteristics analysis. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1992;45:627-37. - PubMed
Rodriguez‐Molinero 2010 {published data only}
-
- Rodriguez-Molinero A, Lopez-Dieguez M, Medina IP, Tabuenca AI, la Cruz JJ, Banegas JR. Cognitive assessment of elderly patients in the emergency department. Revista Espanola de Geriatria y Gerontolgia 2010;45:183-8. - PubMed
Rovner 2012 {published data only}
-
- Rovner BW, Casten RJ, Arenson C, Salzman B, Kornsey EB. Racial differences in the recognition of cognitive dysfunction in older persons. Alzheimer's Disease and Associated Disorders 2012;26:44-9. - PubMed
Sanchez 2009 {published data only}
-
- dos Santos Sanchez MA, Lourenco RA. IQCODE cross cultural adaptation for use in Brazil. Cadernos de Saude Publica 2009;25:1455-65. - PubMed
Schofield 2006 {published data only}
-
- Schoffield PW. Discrepancies in cognitive history from patient and informant in relation to cognitive function. Research and Practice in Alzheimer's Disease 2006;11:328-31.
Sikkes 2010 {published data only}
-
- Sikkes SAM, den Berg MT, Knol DL, de-Lange-de Klerk ESM, Scheltens P, Uitdehaag BMJ et al. How useful is IQCODE for discriminating between Alzheimer's disease, mild cognitive impairment and subjective memory complaints? Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders. 2010;30:411-6. - PubMed
Siri 2006 {published data only}
-
- Siri S, Okanurak K, Chansirikanjana S, Kitiyaporn D, Jorm AF. Modified IQCODE as a screening test for dementia for Thai elderly. Southeast Asian Journal Tropical Medicine and Public Health 2006;37:587-94. - PubMed
Starr 2000 {published data only}
-
- Starr JM, Nicolson C, Anderson K, Dennis MS, Deary IJ. Correlates of informant rated cognitive decline after stroke. Cerebrovsacular Diseases 2000;10:214-20. - PubMed
Tang 2003 {published data only}
-
- Tang WK, Sandra SMC, Chiu HFK, Wong KS, Kwok TCY, Mok V, Ungvari GS. Can IQCODE detect post stroke dementia. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2003;18:706-10. - PubMed
Thomas 1994 {published data only}
-
- Thomas LD, Gonzales MF, Chamberlain A, Beyreuther K, Masters CL, Flicker L. Comparison of clinical state retrospective informant interview and the neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1994;9:233-6.
Tokuhara 2006 {published data only}
-
- Tokuhara KG, Valcour VG, Masaki KH, Blanchette PL. Utility of the IQCODE for dementia in a Japanese American population. Hawai'i Medical Journal 2006;65:72-5. - PubMed
Wierderholt 1999 {published data only}
-
- Wiederholt WC, Galasko D, Salmon DP. Utility of CASI and IQCODE as screening instruments for dementia in natives of Guam. In: abstract (World Congress of Neurology). 1997.
Wolfe 2009 {published data only}
-
- Wolf SA, Kubatschek K, Henry M, Harth S, Edbert AD, Wallesch CW. Informant report of cognitive changes in the elderly. A first evaluation of the German version of the IQCODE. Nervenartz 2009;10:1178-80. - PubMed
Zevallos‐Bustamente 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zevallos Bustamante SE, Bottino CMC, Lopes MA, Dionísio Azevedo D, Hototatian SR, Litvoc J, Filho JW. Combined instruments on the evaluation of dementia in the elderly preliminary results. Arquivos de Neuro-Psiquiatria 2003;61:601-6. - PubMed
Zhang 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zhang XQ, Zhou JS, Wang LD, Meng C, Chen B. Memory complaints in the clinical diagnosis of dementia. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2003;7:4254-5.
Zhou 2002 {published data only}
-
- Zhou JS, Zhang XQ, Wang L. Telephone questionnaire a new method for screening dementia. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2002;6:3166-7.
Zhou 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zhou J, Xinqing Z, Wang L, Meng C, Chu C, Chen B. Orientation memory concentration test and short IQCODE in the elderly screen dementia by telephone. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2003;7:1529-31.
Zhou 2004 {published data only}
-
- Zhou JS, Zhang XQ, Wang L. Telephone IQCODE for dementia. In: abstract. 2004.
Additional references
Birks 2006
Bossuyt 2003
Boustani 2003
-
- Boustani M, Peterson B, Hanson L, Harris R, Lohr KN. Screening for dementia in primary care: a summary of the evidence for the US Preventative Services Task Force. Annals of Internal Medicine 2003;138:927-37. - PubMed
Brodaty 2002
-
- Brodaty H. The GPCOG a new screening test for dementia designed for general practice. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2002;50:530-4. - PubMed
Brunet 2012
-
- Brunet MD, McCartney M, Heath I, Tomlinson J, Cosgrove J, Deveson P et al. Open letter to the Prime Minister and Chief Medical Officer for England. There is no evidence base for proposed dementia screening. BMJ 2012;345:e8588. - PubMed
Chodosh 2004
-
- Chodosh J, Petitti DB, Elliott M, Hays RD, Crooks VC, Reuben DB et al. Physician recognition of cognitive impairment: evaluating the need for improvement. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2004;52:1051-9. - PubMed
Clare 2003
-
- Clare L, Woods B. Cognitive rehabilitation and cognitive training for early-stage Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003;4:CD003260. - PubMed
Cordell 2013
-
- Cordell CB, Borson B, Boustani M, Chodosh J, Reuben D, Verghese J et al, Medicare Detection of Cognitive Impairment Group. Alzheimer's Associaton recommendations for operationalizing the detection of cognitive impairment during the Medicare Annual Wellness Visit in a primary care setting. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2013;9:141-50. - PubMed
Cordoliani‐Mackowiak 2003
-
- Cordoliani-Mackowiak MA, Henon H, Pruvo JP, Pasquier F, Leys D. Poststroke dementia influence of hippocampal atrophy. Archives of Neurology 2003;60:585-90. - PubMed
Cullen 2007
Erkinjuntti 2000
-
- Erkinjuntti T, Inzitari D, Pantoni L. Research criteria for subcortical vascular dementia in clinical trials. Journal of Neural Transmission. Supplementa 2000;59:23–30. - PubMed
Ferri 2005
Folstein 1975
-
- Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. Minimental state: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1975;12:189–98. - PubMed
Galvin 2005
-
- Galvin JE. A brief informant interview to detect dementia. Neurology 2005;65:559-64. - PubMed
Greenhalgh 2005
Hebert 2003
-
- Hebert LE, Scherr PA, Bienas JL, Bennett DA, Evans DA. Alzheimers disease in the US population: prevalence estimates using the 2000 census. Archives of Neurology 2003;60:1119-22. - PubMed
Holsinger 2007
-
- Holsinger T, Deveau J, Boustani M, Willimas JW. Does this patient have dementia. JAMA 2007;21:2391-404. - PubMed
Jorm 1988
-
- Jorm AF, Korten AE. Assessment of cognitive decline in the elderly by informant interview. British Journal of Psychiatry 1988;152:209–13. - PubMed
Jorm 1989A
-
- Jorm AF, Jacomb PA. The informant questionnaire on cognitive decline in the elderly (IQCODE) sociodemographic correlates; reliability; validity and some norms. Psychological Medicine 1989;19:1015-22. - PubMed
Jorm 2000A
-
- Jorm AF, Christensen H, Henderson AS, Jacomb PA, Korten AE, Mackinnon A. Informant ratings of cognitive decline in old age: validation against change on cognitive tests over 7-8 years. Psychological Medicine 2000;30:981-5. - PubMed
Matthews 2013
-
- Matthews FE, Arthur A, Barnes LE, Bond J, Jagger C, Robinson L, Brayne C, Medical Research Council Cognitive Function and Ageing Collaboration. A two-decade comparison of prevalence of dementia in individuals aged 65 years and older from three geographical areas of England: results of the Cognitive Function and Ageing Study I and II. Lancet 2013;382(9902):1405-12. - PMC - PubMed
McKeith 2005
-
- McKeith IG, Dickson DW, Lowe J, Emre M, O’Brien JT, Feldman H. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies third report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 2005;65:1863–72. - PubMed
McKhann 1984
-
- McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology 1984;34(7):939–44. - PubMed
McKhann 2001
-
- McKhann GM, Albert MS, Grossman M, Miller B, Dickson D, Trojanowski JQ, Work Group on Frontotemporal Dementia and PIck’s Disease. Clinical and pathological diagnosis of frontotemporal dementia: report of the Work Group on Frontotemporal Dementia and Pick's Disease. Archives of Neurology 2001;58:1803-9. - PubMed
McKhann 2011
McShane 2006
-
- McShane R, Areosa Sastre A, Minakaran N. Memantine for dementia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006;2:CD003154. - PubMed
Noel‐Storr 2012
-
- Noel-Storr AH, Flicker L, Ritchie CW, Nquyen GH, Gupta T, Wood P et al. Systematic review of the body of evidence for the use of biomarkers in diagnosis of dementia. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2013;9(3):e96-e105. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2012.01.014. - PubMed
Reitsma 2005
-
- Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, Scholten RJ, Bossuyt PM, Zwinderman AH. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58:982-90. - PubMed
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- Review Manager (RevMan) 5.1. The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Copenhagan: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, 2011.
Rockwood 1998
-
- Rockwood K. Retrospective diagnosis of dementia using an informant interview based on the Brief Cgnitive Rating Scale. International Psychogeriatrics 1998;10:53-60. - PubMed
Roman 1993
-
- Roman GC, Tatemichi TK, Erkinjutti T, Cummings JL, Masdeu JC, Garcia JH et al. Vascular dementia: diagnostic criteria for research studies. Report of the NINDS-AIREN International Workshop. Neurology 1993;43:250-60. - PubMed
Savva 2009
-
- Savva GM, Wharton SB, Ince PG, Forster G, Matthews FE, Brayne C et al. Age, neuropathology and dementia. New England Journal of Medicine 2009;360:230-9. - PubMed
Schuetz 2012
Valcour 2000
-
- Valcour VG, Masaki KH, Curb JD, Blanchette PL. The detection of dementia in the primary care setting. Archives of Internal Medicine 2000;160:2964-8. - PubMed
Yamada 2008
-
- Yamada M, Mimori Y, Kasagi F, Miyachi T, Ohshita T, Sudoh S et al. Incidence of dementia, Alzheimers disease and vascular dementia in a Japanese population radiation effects Research Foundation Adult Health Study. Neuroepidemiology 2008;30:152-60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

