Lipids and Lipid Derivatives for RNA Delivery
- PMID: 34279087
- PMCID: PMC10088400
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00244
Lipids and Lipid Derivatives for RNA Delivery
Abstract
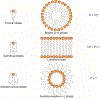
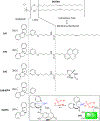
RNA-based therapeutics have shown great promise in treating a broad spectrum of diseases through various mechanisms including knockdown of pathological genes, expression of therapeutic proteins, and programmed gene editing. Due to the inherent instability and negative-charges of RNA molecules, RNA-based therapeutics can make the most use of delivery systems to overcome biological barriers and to release the RNA payload into the cytosol. Among different types of delivery systems, lipid-based RNA delivery systems, particularly lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), have been extensively studied due to their unique properties, such as simple chemical synthesis of lipid components, scalable manufacturing processes of LNPs, and wide packaging capability. LNPs represent the most widely used delivery systems for RNA-based therapeutics, as evidenced by the clinical approvals of three LNP-RNA formulations, patisiran, BNT162b2, and mRNA-1273. This review covers recent advances of lipids, lipid derivatives, and lipid-derived macromolecules used in RNA delivery over the past several decades. We focus mainly on their chemical structures, synthetic routes, characterization, formulation methods, and structure-activity relationships. We also briefly describe the current status of representative preclinical studies and clinical trials and highlight future opportunities and challenges.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Y.D. is a scientific advisory board member of Oncorus Inc and serves as a consultant of Rubius Therapeutics.
Figures


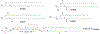


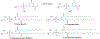


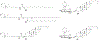





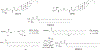

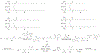

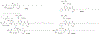


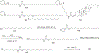
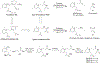

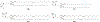
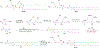




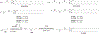
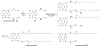


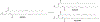







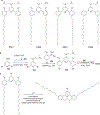
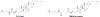






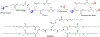









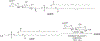

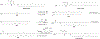

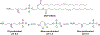



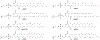

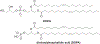
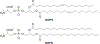
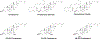


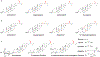

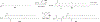






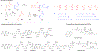

References
-
- DeWitt DE; Hirsch IB Outpatient Insulin Therapy in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. JAMA 2003, 289, 2254–2264. - PubMed
-
- Akhtar MJ; Ahamed M; Kumar S; Siddiqui H; Patil G; Ashquin M; Ahmad I Nanotoxicity of Pure Silica Mediated Through Oxidant Generation Rather Than Glutathione Depletion in Human Lung Epithelial Cells. Toxicology 2010, 276, 95–102. - PubMed
-
- Naldini L Gene Therapy Returns to Centre Stage. Nature 2015, 526, 351–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

