Find Me If You Can: First Clinical Experience Using the Novel CARTOFINDER Algorithm in a Routine Workflow for Atrial Fibrillation Ablation
- PMID: 34279463
- PMCID: PMC8269300
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10132979
Find Me If You Can: First Clinical Experience Using the Novel CARTOFINDER Algorithm in a Routine Workflow for Atrial Fibrillation Ablation
Abstract
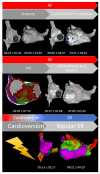
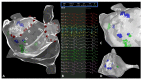
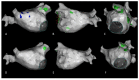
Aims: The CARTOFINDER module allows for simultaneous and automated detection of repetitive focal and rotational activations in patients with atrial arrhythmias. This study aimed to validate the CARTOFINDER algorithm for the detection of potential drivers for atrial fibrillation (AF) and to access their potential impact on individual arrhythmia substrates.
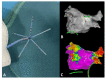
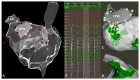
Methods: Fifty consecutive patients underwent AF ablation for persistent AF (PERS), using a 3D-mapping system with the integrated CARTOFINDER module. Regions of interest (ROIs) were identified before and after ablation, and their spatial and temporal relationship was correlated with areas of fibrosis.
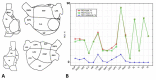
Results: Procedural success was achieved in all patients and 42% received ablation beyond pulmonary vein isolation (PVI). AF termination was observed in 6 patients (12%). The mean procedure duration was 134 ± 29 min. ROIs were revealed in all patients (mean n = 77 ± 52) and there was no statistical evidence for a predilection site. There was no significant anatomical correlation between ROIs and bipolar low voltage. Remapping confirmed the elimination of ROIs in relation to the individual ablation site, a limited reproducibility of rotational ROIs and persistent focal activity over time in some anatomical segments. ROIs were not a predictor for AF recurrence during following ablation.
Conclusions: CARTOFINDER mapping can be integrated into a routine workflow for AF ablation. ROIs could be discriminated in all patients and an ablation effect was observed in some patients, whereas persistent activity was found in certain anatomical segments, even after ablation. ROIs might be an additional ablation target when we are able to understand the individual substrate.
Keywords: CARTOFINDER; atrial fibrillation; catheter ablation; panoramic mapping.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hindricks G., Potpara T., Dagres N., Arbelo E., Bax J.J., Blomstrom-Lundqvist C., Watkins C.L. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart. J. 2021;42:373–498. - PubMed
-
- Sohns C., Zintl K., Zhao Y., Dagher L., Andresen D., Siebels J., Wegscheider K., Sehner S., Boersma L., Merkely B., et al. Impact of left ventricular function and heart failure symptoms on outcomes post ablation of atrial fibrillation in heart failure: CASTLE-AF trial. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2020;13:e008461. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.120.008461. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lim H.S., Hocini M., Dubois R., Denis A., Derval N., Zellerhoff S., Yamashita S., Berte B., Mahida S., Komatsu Y., et al. Complexity and Distribution of Drivers in Relation to Duration of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017;69:1257–1269. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.01.014. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

