Genetic and Biochemical Characterization of the Na+/H+ Antiporters of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 34280000
- PMCID: PMC8378476
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00284-21
Genetic and Biochemical Characterization of the Na+/H+ Antiporters of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
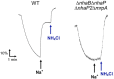
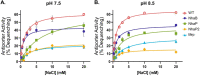
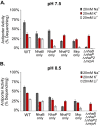
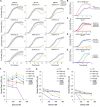
Pseudomonas aeruginosa has four Na+/H+ antiporters that interconvert and balance Na+ and H+ gradients across the membrane. These gradients are important for bioenergetics and ionic homeostasis. To understand these transporters, we constructed four strains, each of which has only one antiporter, i.e., NhaB, NhaP, NhaP2, and Mrp. We also constructed a quadruple deletion mutant that has no Na+/H+ antiporters. Although the antiporters of P. aeruginosa have been studied previously, the strains constructed here present the opportunity to characterize their kinetic properties in their native membranes and their roles in the physiology of P. aeruginosa. The strains expressing only NhaB or Mrp, the two electrogenic antiporters, were able to grow essentially like the wild-type strain across a range of Na+ concentrations and pH values. Strains with only NhaP or NhaP2, which are electroneutral, grew more poorly at increasing Na+ concentrations, especially at high pH values, with the strain expressing NhaP being more sensitive. The strain with no Na+/H+ antiporters was extremely sensitive to the Na+ concentration and showed essentially no Na+(Li+)/H+ antiporter activity, but it retained most K+/H+ antiporter activity of the wild-type strain at pH 7.5 and approximately one-half at pH 8.5. We also used the four strains that each express one of the four antiporters to characterize the kinetic properties of each transporter. Transcriptome sequencing analysis of the quadruple deletion strain showed widespread changes, including changes in pyocyanin synthesis, biofilm formation, and nitrate and glycerol metabolism. Thus, the strains constructed for this study will open a new door to understanding the physiological roles of these proteins and their activities in P. aeruginosa. IMPORTANCE Pseudomonas aeruginosa has four Na+/H+ antiporters that connect and interconvert its Na+ and H+ gradients. We have constructed four deletion mutants, each of which has only one of the four Na+/H+ antiporters. These strains made it possible to study the properties and physiological roles of each antiporter independently in its native membrane. Mrp and NhaB are each able to sustain growth over a wide range of pH values and Na+ concentrations, whereas the two electroneutral antiporters, NhaP and NhaP2, are most effective at low pH values. We also constructed a quadruple mutant lacking all four antiporters, in which the H+ and Na+ gradients are disconnected. This will make it possible to study the role of the two gradients independently.
Keywords: Na+/H+ antiporters; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; energy metabolism; ion transporters.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A major Li(+) extrusion system NhaB of Pseudomonas aeruginosa : comparison with the major Na(+) extrusion system NhaP.Microbiol Immunol. 2004;48(4):243-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2004.tb03520.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15107534
-
Alkaline Response of a Halotolerant Alkaliphilic Halomonas Strain and Functional Diversity of Its Na+(K+)/H+ Antiporters.J Biol Chem. 2016 Dec 9;291(50):26056-26065. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.751016. Epub 2016 Oct 24. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27777302 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and sequencing of a novel Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Jul 9;1398(3):330-4. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(98)00058-x. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998. PMID: 9655928
-
Insights into the biochemistry of the ubiquitous NhaP family of cation/H+ antiporters.Biochem Cell Biol. 2011 Apr;89(2):130-7. doi: 10.1139/o10-149. Biochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21455265 Review.
-
The role of monovalent cation/proton antiporters in Na(+)-resistance and pH homeostasis in Bacillus: an alkaliphile versus a neutralophile.J Exp Biol. 1994 Nov;196:457-70. doi: 10.1242/jeb.196.1.457. J Exp Biol. 1994. PMID: 7823040 Review.
Cited by
-
Prokaryotic Na+/H+ Exchangers-Transport Mechanism and Essential Residues.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 15;23(16):9156. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169156. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the genome of Methylobacterium sp. NMS14P, a novel bacterium for growth promotion of maize, chili, and sugarcane.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 7;18(2):e0281505. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281505. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36749783 Free PMC article.
-
Novel NhaC Na+/H+ antiporter in cyanobacteria contributes to key molecular processes for salt tolerance.Plant Mol Biol. 2024 Oct 15;114(6):111. doi: 10.1007/s11103-024-01510-4. Plant Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39404982
-
A Halophilic Bacterium for Bioremediation of Saline-Alkali Land: The Triadic and Synergetic Response Mechanism of Oceanobacillus picturae DY09 to Salt Stress.Microorganisms. 2025 Jun 25;13(7):1474. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13071474. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40731984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grosso-Becerra MV, Santos-Medellín C, González-Valdez A, Méndez JL, Delgado G, Morales-Espinosa R, Servín-González L, Alcaraz LD, Soberón-Chávez G. 2014. Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical and environmental isolates constitute a single population with high phenotypic diversity. BMC Genomics 15:318. 10.1186/1471-2164-15-318. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Weiner-Lastinger LM, Abner S, Edwards JR, Kallen AJ, Karlsson M, Magill SS, Pollock D, See I, Soe MM, Walters MS, Dudeck MA. 2020. Antimicrobial-resistant pathogens associated with adult healthcare-associated infections: summary of data reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network, 2015–2017. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 41:1–18. 10.1017/ice.2019.296. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

