BTK inhibition sensitizes acute lymphoblastic leukemia to asparaginase by suppressing the amino acid response pathway
- PMID: 34280258
- PMCID: PMC8832462
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2021011787
BTK inhibition sensitizes acute lymphoblastic leukemia to asparaginase by suppressing the amino acid response pathway
Abstract
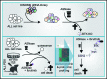
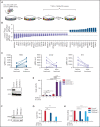
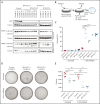
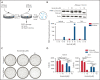
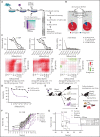
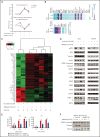
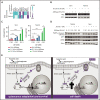
Asparaginase (ASNase) therapy has been a mainstay of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) protocols for decades and shows promise in the treatment of a variety of other cancers. To improve the efficacy of ASNase treatment, we used a CRISPR/Cas9-based screen to identify actionable signaling intermediates that improve the response to ASNase. Both genetic inactivation of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) and pharmacological inhibition by the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib strongly synergize with ASNase by inhibiting the amino acid response pathway, a mechanism involving c-Myc-mediated suppression of GCN2 activity. This synthetic lethal interaction was observed in 90% of patient-derived xenografts, regardless of the genomic subtype. Moreover, ibrutinib substantially improved ASNase treatment response in a murine PDX model. Hence, ibrutinib may be used to enhance the clinical efficacy of ASNase in ALL. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as # NCT02884453.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
References
-
- Covini D, Tardito S, Bussolati O, et al. Expanding targets for a metabolic therapy of cancer: L-asparaginase. Recent Patents Anticancer Drug Discov. 2012;7(1):4-13. - PubMed
-
- Fernandes HS, Silva Teixeira CS, Fernandes PA, Ramos MJ, Cerqueira NM. Amino acid deprivation using enzymes as a targeted therapy for cancer and viral infections. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017;27(3):283-297. - PubMed
-
- Henriksen LT, Nersting J, Raja RA, et al. ; Nordic Society of Paediatric Haematology and Oncology (NOPHO) group . Cerebrospinal fluid asparagine depletion during pegylated asparaginase therapy in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2014;166(2):213-220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

