The Psychological Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Women's Mental Health during Pregnancy: A Rapid Evidence Review
- PMID: 34281049
- PMCID: PMC8297318
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18137112
The Psychological Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Women's Mental Health during Pregnancy: A Rapid Evidence Review
Abstract
Background: The perinatal period is a particularly vulnerable period in women's lives that implies significant physiological and psychological changes that can place women at higher risk for depression and anxiety symptoms. In addition, the ongoing pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is likely to increase this vulnerability and the prevalence of mental health problems. This review aimed to investigate the existing literature on the psychological impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on women during pregnancy and the first year postpartum.
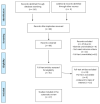
Method: The literature search was conducted using the following databases: Pubmed, Scopus, WOS-web of science, PsycInfo and Google Scholar. Out of the total of 116 initially selected papers, 17 have been included in the final work, according to the inclusion criteria.
Results: The reviewed contributions report a moderate to severe impact of the COVID-19 outbreak on the mental health of pregnant women, mainly in the form of a significant increase in depression-up to 58% in Spain-and anxiety symptoms-up to 72% in Canada. In addition to the common psychological symptoms, COVID-19-specific worries emerged with respect to its potential effects on pregnancy and the well-being of the unborn child. Social support and being engaged in regular physical activities appear to be protective factors able to buffer against the effects of the pandemic on maternal mental health.
Conclusions: Despite the limitations of the study design, the evidence suggests that it is essential to provide appropriate psychological support to pregnant women during the emergency in order to protect their mental health and to minimize the risks of long-term effects on child development.
Keywords: COVID-19; anxiety; depression; maternal mental health; perinatality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kajdy A., Feduniw S., Ajdacka U., Modzelewski J., Baranowska B., Sys D., Pokropek A., Pawlicka P., Kaźmierczak M., Rabijewski M., et al. Risk factors for anxiety and depression among pregnant women during the COVID-19 pandemic: A web-based cross-sectional survey. Medicine. 2020;99:e21279. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021279. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical