Overlap Arrhythmia Syndromes Resulting from Multiple Genetic Variations Studied in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 34281161
- PMCID: PMC8268422
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22137108
Overlap Arrhythmia Syndromes Resulting from Multiple Genetic Variations Studied in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes
Abstract
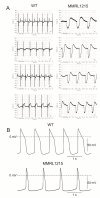
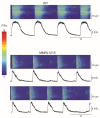
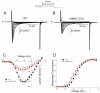
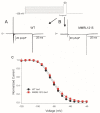
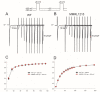
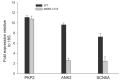
Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) are used for genetic models of cardiac diseases. We report an arrhythmia syndrome consisting of Early Repolarization Syndrome (ERS) and Short QT Syndrome (SQTS). The index patient (MMRL1215) developed arrhythmia-mediated syncope after electrocution and was found to carry six mutations. Functional alterations resulting from these mutations were examined in patient-derived hiPSC-CMs. Electrophysiological recordings were made in hiPSC-CMs from MMRL1215 and healthy controls. ECG analysis of the index patient showed slurring of the QRS complex and QTc = 326 ms. Action potential (AP) recordings from MMRL1215 myocytes showed slower spontaneous activity and AP duration was shorter. Field potential recordings from MMRL1215 hiPSC-CMs lack a "pseudo" QRS complex suggesting reduced inward current(s). Voltage clamp analysis of ICa showed no difference in the magnitude of current. Measurements of INa reveal a 60% reduction in INa density in MMRL1215 hiPSC-CMs. Steady inactivation and recovery of INa was unaffected. mRNA analysis revealed ANK2 and SCN5A are significantly reduced in hiPSC-CM derived from MMRL1215, consistent with electrophysiological recordings. The polygenic cause of ERS/SQTS phenotype is likely due to a loss of INa due to a mutation in PKP2 coupled with and a gain of function in IK,ATP due to a mutation in ABCC9.
Keywords: action potentials; depolarization; electrophysiology; sodium current; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no relationships that can be construed as a conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Terrenoire C., Wang K., Tung K.W.C., Chung W.K., Pass R.H., Lu J.T., Jean J.-C., Omari A., Sampson K.J., Kotton D., et al. Induced pluripotent stem cells used to reveal drug actions in a long QT syndrome family with complex genetics. J. Gen. Physiol. 2012;141:61–72. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201210899. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

