Basic Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) Transcription Factors Regulate a Wide Range of Functions in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 34281206
- PMCID: PMC8267941
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22137152
Basic Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) Transcription Factors Regulate a Wide Range of Functions in Arabidopsis
Abstract
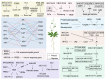
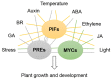
The basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor family is one of the largest transcription factor gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana, and contains a bHLH motif that is highly conserved throughout eukaryotic organisms. Members of this family have two conserved motifs, a basic DNA binding region and a helix-loop-helix (HLH) region. These proteins containing bHLH domain usually act as homo- or heterodimers to regulate the expression of their target genes, which are involved in many physiological processes and have a broad range of functions in biosynthesis, metabolism and transduction of plant hormones. Although there are a number of articles on different aspects to provide detailed information on this family in plants, an overall summary is not available. In this review, we summarize various aspects of related studies that provide an overview of insights into the pleiotropic regulatory roles of these transcription factors in plant growth and development, stress response, biochemical functions and the web of signaling networks. We then provide an overview of the functional profile of the bHLH family and the regulatory mechanisms of other proteins.
Keywords: basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH); cross-talk; plant growth and development; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

