Bisphenol A Modulates Autophagy and Exacerbates Chronic Kidney Damage in Mice
- PMID: 34281243
- PMCID: PMC8268806
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22137189
Bisphenol A Modulates Autophagy and Exacerbates Chronic Kidney Damage in Mice
Abstract
Background: Bisphenol A (BPA) is a ubiquitous environmental toxin that accumulates in chronic kidney disease (CKD). Our aim was to explore the effect of chronic exposition of BPA in healthy and injured kidney investigating potential mechanisms involved.
Methods: In C57Bl/6 mice, administration of BPA (120 mg/kg/day, i.p for 5 days/week) was done for 2 and 5 weeks. To study BPA effect on CKD, a model of subtotal nephrectomy (SNX) combined with BPA administration for 5 weeks was employed. In vitro studies were done in human proximal tubular epithelial cells (HK-2 line).
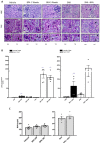
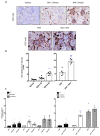
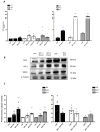
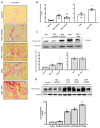
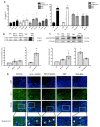
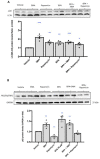
Results: Chronic BPA administration to healthy mice induces inflammatory infiltration in the kidney, tubular injury and renal fibrosis (assessed by increased collagen deposition). Moreover, in SNX mice BPA exposure exacerbates renal lesions, including overexpression of the tubular damage biomarker Hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 1 (Havcr-1/KIM-1). BPA upregulated several proinflammatory genes and increased the antioxidant response [Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), Heme Oxygenase-1 (Ho-1) and NAD(P)H dehydrogenase quinone 1 (Nqo-1)] both in healthy and SNX mice. The autophagy process was modulated by BPA, through elevated autophagy-related gene 5 (Atg5), autophagy-related gene 7 (Atg7), Microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3B (Map1lc3b/Lc3b) and Beclin-1 gene levels and blockaded the autophagosome maturation and flux (p62 levels). This autophagy deregulation was confirmed in vitro.
Conclusions: BPA deregulates autophagy flux and redox protective mechanisms, suggesting a potential mechanism of BPA deleterious effects in the kidney.
Keywords: Bisphenol A; autophagy; fibrosis; inflammation; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

