Diffusion-weighted MRI and 18F-FDG PET/CT in assessing the response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 34281566
- PMCID: PMC8287821
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-021-01852-z
Diffusion-weighted MRI and 18F-FDG PET/CT in assessing the response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) followed by surgery is a currently widely used strategy for locally advanced esophageal cancer (EC). However, the conventional imaging methods have certain deficiencies in the evaluation and prediction of the efficacy of nCRT. This study aimed to explore the value of functional imaging in predicting the response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
Methods: Fifty-four patients diagnosed with locally advanced ESCC from August 2017 to September 2019 and treated with nCRT were retrospectively analyzed. DW-MRI scanning was performed before nCRT, at 10-15 fractions of radiotherapy, and 4-6 weeks after the completion of nCRT. 18F-FDG PET/CT scans were performed before nCRT and 4-6 weeks after the completion of nCRT. These 18F-FDG PET/CT and DW-MRI parameters and relative changes were compared between patients with pathological complete response (pCR) and non-pCR.
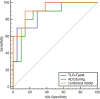
Results: A total of 8 of 54 patients (14.8%) were evaluated as disease progression in the preoperative assessment. The remaining forty-six patients underwent operations, and the pathological assessments of the surgical resection specimens demonstrated pathological complete response (pCR) in 10 patients (21.7%) and complete response of primary tumor (pCR-T) in 16 patients (34.8%). The change of metabolic tumor volume (∆MTV) and change of total lesion glycolysis (∆TLG) were significantly different between patients with pCR and non-pCR. The SUVmax-Tpost, MTV-Tpost, and TLG-Tpost of esophageal tumors in 18F-FDG PET/CT scans after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and the ∆ SUVmax-T and ∆MTV-T were significantly different between pCR-T versus non-pCR-T patients. The esophageal tumor apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) increased after nCRT; the ADCduring, ADCpost and ∆ADCduring were significantly different between pCR-T and non-pCR-T groups. ROC analyses showed that the model that combined ADCduring with TLG-Tpost had the highest AUC (0.914) for pCR-T prediction, with 90.0% and 86.4% sensitivity and specificity, respectively.
Conclusion: 18F-FDG PET/CT is useful for re-staging after nCRT and for surgical decision. Integrating parameters of 18F-FDG PET/CT and DW-MRI can identify pathological response of primary tumor to nCRT more accurately in ESCC.
Keywords: 18F-FDG PET/CT; DW-MRI; Esophageal squamous cell cancer; Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy; Pathological complete response.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Preoperative Prediction of Pathologic Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Patients With Esophageal Cancer Using 18F-FDG PET/CT and DW-MRI: A Prospective Multicenter Study.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020 Apr 1;106(5):998-1009. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.12.038. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020. PMID: 31987972 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
FDG PET using SUVmax for preoperative T-staging of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma with and without neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy.BMC Med Imaging. 2017 Jan 5;17(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12880-016-0171-7. BMC Med Imaging. 2017. PMID: 28056868 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Predictive Immune and Metabolic Biomarkers of Tumor Microenvironment Regarding Pathological and Clinical Response in Esophageal Cancer After Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy: A Systematic Review.Ann Surg Oncol. 2024 Jan;31(1):433-451. doi: 10.1245/s10434-023-14352-z. Epub 2023 Sep 30. Ann Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 37777688 Free PMC article.
-
The role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in predicting the pathological response to neoadjuvant PD-1 blockade in combination with chemotherapy for resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022 Oct;49(12):4241-4251. doi: 10.1007/s00259-022-05872-z. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35732974
-
Accuracy of Detecting Residual Disease After Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy for Esophageal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Ann Surg. 2020 Feb;271(2):245-256. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003397. Ann Surg. 2020. PMID: 31188203
Cited by
-
The application of radiomics in esophageal cancer: Predicting the response after neoadjuvant therapy.Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 6;13:1082960. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1082960. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37091180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nomogram for predicting pathologic complete response following preoperative chemoradiotherapy in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2024 Jul 6;12:goae060. doi: 10.1093/gastro/goae060. eCollection 2024. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2024. PMID: 38974878 Free PMC article.
-
Chemoradiotherapy with paclitaxel liposome plus cisplatin for locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective analysis.Cancer Med. 2023 Mar;12(6):6477-6487. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5416. Epub 2022 Nov 22. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37012831 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing Esophageal Cancer Staging and Restaging: The Role of MRI in Precision Diagnosis.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 17;17(8):1351. doi: 10.3390/cancers17081351. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40282527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual energy CT-derived quantitative parameters and hematological characteristics predict pathological complete response in neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 May 10;25(1):357. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03964-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40349002 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

