Prevalence of childhood mental disorders in high-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis to inform policymaking
- PMID: 34281985
- PMCID: PMC8788041
- DOI: 10.1136/ebmental-2021-300277
Prevalence of childhood mental disorders in high-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis to inform policymaking
Abstract
Question: Mental disorders typically start in childhood and persist, causing high individual and collective burdens. To inform policymaking to address children's mental health in high-income countries we aimed to identify updated data on disorder prevalence.
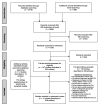
Methods: We identified epidemiological studies reporting mental disorder prevalence in representative samples of children aged 18 years or younger-including a range of disorders and ages and assessing impairment (searching January 1990 through February 2021). We extracted associated service-use data where studies assessed this. We conducted meta-analyses using a random effects logistic model (using R metafor package).
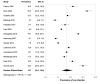
Findings: Fourteen studies in 11 countries met inclusion criteria, published from 2003 to 2020 with a pooled sample of 61 545 children aged 4-18 years, including eight reporting service use. (All data were collected pre-COVID-19.) Overall prevalence of any childhood mental disorder was 12.7% (95% CI 10.1% to 15.9%; I2=99.1%). Significant heterogeneity pertained to diagnostic measurement and study location. Anxiety (5.2%), attention-deficit/hyperactivity (3.7%), oppositional defiant (3.3%), substance use (2.3%), conduct (1.3%) and depressive (1.3%) disorders were the most common. Among children with mental disorders, only 44.2% (95% CI 37.6% to 50.9%) received any services for these conditions.
Conclusions: An estimated one in eight children have mental disorders at any given time, causing symptoms and impairment, therefore requiring treatment. Yet even in high-income countries, most children with mental disorders are not receiving services for these conditions. We discuss the implications, particularly the need to substantially increase public investments in effective interventions. We also discuss the policy urgency, given the emerging increases in childhood mental health problems since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic (PROSPERO CRD42020157262).
Keywords: child & adolescent psychiatry.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: KG and CW participated in the Ontario Child Health Study [reference s8] as Co-Principal Investigator and Co-Investigator, respectively. They therefore did not participate in decisions about inclusion, data extraction or interpretations regarding this study. KG was also an author on one other included study [reference s10] and did not participate in decisions about inclusion, data extraction or interpretation regarding this study. These two authors have no other conflicts to declare. All other authors declare no conflicts.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
