Long-term decrease in Asian monsoon rainfall and abrupt climate change events over the past 6,700 years
- PMID: 34282014
- PMCID: PMC8325342
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2102007118
Long-term decrease in Asian monsoon rainfall and abrupt climate change events over the past 6,700 years
Abstract
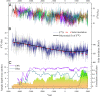
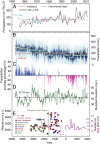
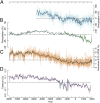
Asian summer monsoon (ASM) variability and its long-term ecological and societal impacts extending back to Neolithic times are poorly understood due to a lack of high-resolution climate proxy data. Here, we present a precisely dated and well-calibrated tree-ring stable isotope chronology from the Tibetan Plateau with 1- to 5-y resolution that reflects high- to low-frequency ASM variability from 4680 BCE to 2011 CE. Superimposed on a persistent drying trend since the mid-Holocene, a rapid decrease in moisture availability between ∼2000 and ∼1500 BCE caused a dry hydroclimatic regime from ∼1675 to ∼1185 BCE, with mean precipitation estimated at 42 ± 4% and 5 ± 2% lower than during the mid-Holocene and the instrumental period, respectively. This second-millennium-BCE megadrought marks the mid-to late Holocene transition, during which regional forests declined and enhanced aeolian activity affected northern Chinese ecosystems. We argue that this abrupt aridification starting ∼2000 BCE contributed to the shift of Neolithic cultures in northern China and likely triggered human migration and societal transformation.
Keywords: Asian summer monsoon; climate variability; megadrought; stable isotopes; tree rings.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Büntgen U., et al. ., 2500 years of European climate variability and human susceptibility. Science 331, 578–582 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Büntgen U., et al. ., Cooling and societal change during the Late Antique Little Ice Age from 536 to around 660 AD. Nat. Geosci. 9, 231–236 (2016).
-
- deMenocal P. B., Cultural responses to climate change during the late Holocene. Science 292, 667–673 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Stenseth N. C., et al. ., Ecological effects of climate fluctuations. Science 297, 1292–1296 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

