Skin tolerant inactivation of multiresistant pathogens using far-UVC LEDs
- PMID: 34282225
- PMCID: PMC8290050
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-94070-2
Skin tolerant inactivation of multiresistant pathogens using far-UVC LEDs
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Skin tolerant inactivation of multiresistant pathogens using far-UVC LEDs.Sci Rep. 2022 May 11;12(1):7702. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11796-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35545652 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
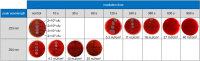
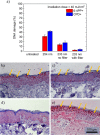
Multiresistant pathogens such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) cause serious postoperative infections. A skin tolerant far-UVC (< 240 nm) irradiation system for their inactivation is presented here. It uses UVC LEDs in combination with a spectral filter and provides a peak wavelength of 233 nm, with a full width at half maximum of 12 nm, and an irradiance of 44 µW/cm2. MRSA bacteria in different concentrations on blood agar plates were inactivated with irradiation doses in the range of 15-40 mJ/cm2. Porcine skin irradiated with a dose of 40 mJ/cm2 at 233 nm showed only 3.7% CPD and 2.3% 6-4PP DNA damage. Corresponding irradiation at 254 nm caused 15-30 times higher damage. Thus, the skin damage caused by the disinfectant doses is so small that it can be expected to be compensated by the skin's natural repair mechanisms. LED-based far-UVC lamps could therefore soon be used in everyday clinical practice to eradicate multiresistant pathogens directly on humans.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Political declaration on antimicrobial resistance, United Nations General Assembly, 71st session, Sept 22, 2016, Agenda item 127, A/71/L.2.
-
- O’Neill, J., Review On Antimicrobial Resistance (London, Grande-Bretagne & Wellcome Trust (London. Antimicrobial resistance: tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations: december 2014. (Review On Antimicrobial Resistance, 2014). https://wellcomecollection.org/works/rdpck35v
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

