Pro-resolving lipid mediators: regulators of inflammation, metabolism and kidney function
- PMID: 34282342
- PMCID: PMC8287849
- DOI: 10.1038/s41581-021-00454-y
Pro-resolving lipid mediators: regulators of inflammation, metabolism and kidney function
Abstract
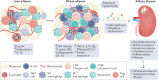
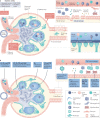
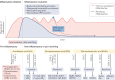
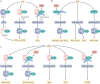
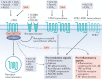
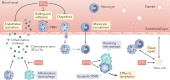
Obesity, diabetes mellitus, hypertension and cardiovascular disease are risk factors for chronic kidney disease (CKD) and kidney failure. Chronic, low-grade inflammation is recognized as a major pathogenic mechanism that underlies the association between CKD and obesity, impaired glucose tolerance, insulin resistance and diabetes, through interaction between resident and/or circulating immune cells with parenchymal cells. Thus, considerable interest exists in approaches that target inflammation as a strategy to manage CKD. The initial phase of the inflammatory response to injury or metabolic dysfunction reflects the release of pro-inflammatory mediators including peptides, lipids and cytokines, and the recruitment of leukocytes. In self-limiting inflammation, the evolving inflammatory response is coupled to distinct processes that promote the resolution of inflammation and restore homeostasis. The discovery of endogenously generated lipid mediators - specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators and branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids - which promote the resolution of inflammation and attenuate the microvascular and macrovascular complications of obesity and diabetes mellitus highlights novel opportunities for potential therapeutic intervention through the targeting of pro-resolution, rather than anti-inflammatory pathways.
© 2021. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gregg, E. W., Hora, I. & Benoit, S. R. Resurgence in diabetes-related complications. 321, 1867–1868 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

