Transcriptional regulation of N6-methyladenosine orchestrates sex-dimorphic metabolic traits
- PMID: 34282353
- PMCID: PMC8422857
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-021-00427-2
Transcriptional regulation of N6-methyladenosine orchestrates sex-dimorphic metabolic traits
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Transcriptional regulation of N6-methyladenosine orchestrates sex-dimorphic metabolic traits.Nat Metab. 2022 Jul;4(7):960. doi: 10.1038/s42255-022-00614-9. Nat Metab. 2022. PMID: 35851380 No abstract available.
-
Author Correction: Transcriptional regulation of N6-methyladenosine orchestrates sex-dimorphic metabolic traits.Nat Metab. 2023 Mar;5(3):530. doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00748-4. Nat Metab. 2023. PMID: 36814000 No abstract available.
Abstract
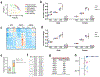
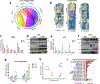
Males and females exhibit striking differences in the prevalence of metabolic traits including hepatic steatosis, a key driver of cardiometabolic morbidity and mortality. RNA methylation is a widespread regulatory mechanism of transcript turnover. Here, we show that presence of the RNA modification N6-methyladenosine (m6A) triages lipogenic transcripts for degradation and guards against hepatic triglyceride accumulation. In male but not female mice, this protective checkpoint stalls under lipid-rich conditions. Loss of m6A control in male livers increases hepatic triglyceride stores, leading to a more 'feminized' hepatic lipid composition. Crucially, liver-specific deletion of the m6A complex protein Mettl14 from male and female mice significantly diminishes sex-specific differences in steatosis. We further surmise that the m6A installing machinery is subject to transcriptional control by the sex-responsive BCL6-STAT5 axis in response to dietary conditions. These data show that m6A is essential for precise and synchronized control of lipogenic enzyme activity and provide insights into the molecular basis for the existence of sex-specific differences in hepatic lipid traits.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests:
J.C. is a scientific founder of Genovel Biotech Corp. and holds equities with the company, and is also a Scientific Advisor for Race Oncology. A patent related to this work is issued to T.S. The other authors declare no competing conflict of interest.
Figures
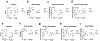









Similar articles
-
Male-specific hepatic Bcl6: growth hormone-induced block of transcription elongation in females and binding to target genes inversely coordinated with STAT5.Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Nov;23(11):1914-26. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0242. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Mol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19797429 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Hepatic Lipid Metabolism Disorder by Modification of m6 A RNA Methylation in Piglets.Lipids. 2018 Jan;53(1):53-63. doi: 10.1002/lipd.12023. Lipids. 2018. PMID: 29488640
-
Dynamic, sex-differential STAT5 and BCL6 binding to sex-biased, growth hormone-regulated genes in adult mouse liver.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Feb;32(4):880-96. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06312-11. Epub 2011 Dec 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22158971 Free PMC article.
-
m6A RNA Methylation and Implications for Hepatic Lipid Metabolism.DNA Cell Biol. 2024 Jun;43(6):271-278. doi: 10.1089/dna.2023.0410. Epub 2024 Apr 18. DNA Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38635960 Review.
-
RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation.Genes Dev. 2015 Jul 1;29(13):1343-55. doi: 10.1101/gad.262766.115. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 26159994 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Function of m6A and its regulation of domesticated animals' complex traits.J Anim Sci. 2022 Mar 1;100(3):skac034. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac034. J Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 35137116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative analysis reveals multiple modes of LXR transcriptional regulation in liver.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Feb 15;119(7):e2122683119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2122683119. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35145035 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of chromosomal sex on cardiometabolic health and disease.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Oct;34(10):652-665. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2023.07.003. Epub 2023 Aug 17. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 37598068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of hepatic steatosis in male and female mule ducks after respective force-feeding programs.Front Physiol. 2024 Jun 21;15:1392968. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1392968. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38974520 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Dimorphism in Brain Sirtuin-1 and m6A Methylated Sirtuin-1 mRNA, and in Protection with Post-Injury Anti-miR-200c treatment, after Experimental Stroke in Aged Mice.Aging Dis. 2023 Jun 1;14(3):892-903. doi: 10.14336/AD.2022.1225. Aging Dis. 2023. PMID: 37191419 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

