Atherogenic indices in non-arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy
- PMID: 34282389
- PMCID: PMC8243175
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2021.07.12
Atherogenic indices in non-arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the atherogenic indices and the relationship with visual acuity and bilateral sequential involvement in patients with non-arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION).
Methods: A total of 65 patients with NAION and 48 age-sex matched healthy individuals were included in this retrospective study. The demographic characteristics and laboratory findings of the patients and control subjects were obtained from the electronic medical records. The atherogenic indices were calculated using the lipid parameters. The association between visual acuity, bilateral sequential involvement, and atherogenic indices was investigated.
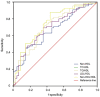
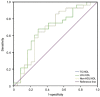
Results: The mean age was 63.8±12.5y in the NAION group and 64.7±10.1y in control group (P=0.707). Although there were no significant differences in terms of total cholesterol (TC) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) between two groups (P=0.089, 0.091), all the non-traditional serum lipid ratios were significantly higher in NAION group (P<0.05). In the NAION subgroup analysis, with visual acuity≤20/200 had higher TC/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c), LDL-c/HDL-c, and non-HDL-c/HDL-c values than the patients in the NAION group with visual acuity >20/200 (P=0.032, 0.025, 0.032, respectively). The values for the atherogenic indices were higher in NAION patients with bilateral sequential involvement in comparison to those with unilateral involvement (P=0.271, 0.127, 0.197, 0.128, 0.127, respectively).
Conclusion: The study reveals a relationship between NAION and the non-traditional lipid ratios. Atherogenic indices may predict the visual loss severity and second eye involvement in patients with NAION.
Keywords: atherogenic index; atherosclerosis; lipid profile; non-arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy; second eye involvement.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of Lipid Parameters on Visual Acuity Change in Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy.Clin Ophthalmol. 2024 Dec 16;18:3791-3800. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S500368. eCollection 2024. Clin Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39712368 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer loss and visual outcome in fellow eyes following sequential bilateral non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy.Curr Eye Res. 2015 May;40(6):632-7. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2014.952829. Epub 2014 Aug 25. Curr Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 25153943
-
The correlation between non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy and cerebral infarction.Transl Neurosci. 2023 Mar 18;14(1):20220281. doi: 10.1515/tnsci-2022-0281. eCollection 2023 Jan 1. Transl Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36949871 Free PMC article.
-
The Association Between Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitor Use and Risk of Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Sex Med. 2018 Sep;6(3):185-192. doi: 10.1016/j.esxm.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Sex Med. 2018. PMID: 29884471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Nonarteritic ischemic optic neuropathy animal model and its treatment applications].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2014 Apr;118(4):331-61. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2014. PMID: 24864434 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Impact of Lipid Parameters on Visual Acuity Change in Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy.Clin Ophthalmol. 2024 Dec 16;18:3791-3800. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S500368. eCollection 2024. Clin Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39712368 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic syndrome and its components are associated with non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy.BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2022 Oct;7(1):e001111. doi: 10.1136/bmjophth-2022-001111. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 36437528 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Associated With the Use of Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors: A Literature Review.Cureus. 2022 Aug 3;14(8):e27642. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27642. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36072219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NA-AION): A Comprehensive Overview.Vision (Basel). 2023 Nov 9;7(4):72. doi: 10.3390/vision7040072. Vision (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37987292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Value of Plasma Atherogenic Index in Prognosis of Sudden Hearing Loss.J Int Adv Otol. 2024 Jan;20(1):30-34. doi: 10.5152/iao.2024.231246. J Int Adv Otol. 2024. PMID: 38454286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buono LM, Foroozan R, Sergott RC, Savino PJ. Nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2002;13(6):357–361. - PubMed
-
- Newman NJ, Scherer R, Langenberg P, Kelman S, Feldon S, Kaufman D, Dickersin K, Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Decompression Trial Research Group The fellow eye in naion: report from the ischemic optic neuropathy decompression trial follow-up study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002;134(3):317–328. - PubMed
-
- Balducci N, Morara M, Veronese C, Barboni P, Casadei NL, Savini G, Parisi V, Sadun AA, Ciardella A. Optical coherence tomography angiography in acute arteritic and non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017;255(11):2255–2261. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources