Retention of different temporary cements tested on zirconia crowns and titanium abutments in vitro
- PMID: 34282495
- PMCID: PMC8289925
- DOI: 10.1186/s40729-021-00349-4
Retention of different temporary cements tested on zirconia crowns and titanium abutments in vitro
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of the present study was to examine the retention force of monolithic zirconia copings cemented with various temporary cements on implant abutments in vitro.
Methods: Sixty exercise implants with pre-screwed implant abutments were embedded in resin. Subsequently, 60 CAD/CAM manufactured zirconia copings were divided into three main groups [Harvard Implant Semi-permanent (HAV), implantlink semi Forte (IMP), Temp Bond NE (TBNE)]. The zirconia copings were cemented on the implant abutments and loaded with 35 N. Specimens were stored in distilled water (37 °C) for 24 h. Half of the test specimens of each group were subjected to a thermocycling (TC) process. Retention force was measured in a universal testing machine. Using magnifying glasses, the fracture mode was determined. Statistical analysis was performed applying the Kruskal-Wallis test, the post hoc test according to Dunn-Bonferroni and a chi-square test of independence.
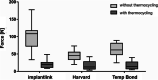
Results: Without TC, IMP showed the highest retention of the three temporary luting agents (100.5 ± 39.14 N). The measured retention forces of IMP were higher than those of HAV (45.78 ± 15.66 N) and TBNE (61.16 ± 20.19 N). After TC, retention was reduced. IMP showed the greatest retentive strength (21.69 ± 13.61 N, three fail outs). HAV and TBNE showed pull-off forces of similar magnitude (17.38 ± 12.77 N and 16.97 ± 12.36 N, two fail outs). The fracture mode analysis showed different results regarding the tested cements before and after TC (facture type before/after TC): IMP (III+II/III), HAV (I/II) and TBNE (III/III). There were clear differences of the fracture modes regarding the examination before and after TC.
Conclusions: Within the limits of this study, IMP showed the highest pull-off forces under the chosen test conditions. All three temporary luting agents showed lower retention forces after TC. Retention values in the individual cement classes were very heterogeneous. Easy cement removal in the crown lumen favours the dominance of adhesive cement fractures on the abutment and adhesive/cohesive cement fractures on the abutment with HAV appears advantageous in case of recementation of the superstructure.
Keywords: Fracture mode analysis; Implantology; Retention; Temporary cements; Titanium; Zirconia crowns.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Felix Dähne, Heike Meißner, Klaus Böning, Christin Arnold, Ralf Gutwald and Elisabeth Prause declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Chee W, Felton DA, Johnson PF, Sullivan DY. Cemented versus screw-retained implant prostheses: which is better? Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1999;14(1):137–141. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

