Real-World Treatment Patterns and Overall Survival of Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer in the US Prior to PARP Inhibitors
- PMID: 34282527
- PMCID: PMC8342357
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-021-01823-6
Real-World Treatment Patterns and Overall Survival of Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer in the US Prior to PARP Inhibitors
Abstract
Introduction: Therapeutic options for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) patients are continuously advancing. We described mCRPC treatment patterns in the US from 2013 to 2019.
Methods: Patients with a confirmed mCRPC diagnosis and adenocarcinoma histology were included in the US Flatiron Health Electronic Health Record-derived de-identified database. Treatment patterns [including treatment per lines of therapies (LOTs), LOT sequences, and time on treatment] and overall survival (OS) have been described in mCRPC settings.
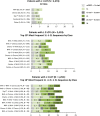
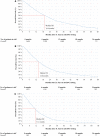
Results: Of 5213 patients (mean age: 72.6 years), 4374 (83.9%) were treated with ≥ 1 LOT post-mCRPC diagnosis (among those with ≥ 1 LOT, 55.3%, 29.5%, 14.7%, and 6.7% had ≥ 2, 3, 4, and 5 LOTs, respectively). In first line (1L), the main treatment class was next-generation hormonal agents (NHA; 62.5% of patients with ≥ 1 LOT), while the shortest and longest time on 1L were observed for chemotherapy (median 2.8 months) and NHA (median 5.1 months), respectively. The most common LOT sequences were NHA → NHA (29.4% of patients with ≥ 2 LOTs) and NHA → NHA → chemotherapy (16.7% of patients with ≥ 3 LOTs). In Kaplan-Meier analyses, the median OS was 19.4, 14.6, and 11.1 months post-1L, 2L, and 3L start, respectively. Patients who moved rapidly through LOTs had an increased risk of death.
Conclusions: NHA were widely used as 1L therapy in mCRPC patients from 2013 to 2019, but time on 1L NHA treatment was on average < 6 months. While NHA → NHA was the most observed 1L → 2L LOT sequence, a plethora of other LOT sequences were observed. OS was poor, highlighting an unmet need for life-prolonging treatments.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Electronic medical records; Lines of therapy; Next-generation hormonal agents; Treatment duration.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Figures


References
-
- https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/prost.html. Accessed Sep 24, 2020.
-
- Centers for disease control and prevention: prostate cancer statistics. 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/prostate/statistics/index.htm. Accessed Jul 13, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

