Tubulointerstitial nephritis in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis with monoclonal gammopathy
- PMID: 34282535
- PMCID: PMC8811071
- DOI: 10.1007/s13730-021-00620-y
Tubulointerstitial nephritis in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis with monoclonal gammopathy
Abstract
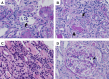
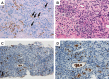
Isolated tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) without glomerular crescent formation is a rare manifestation of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV). Some patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance present with renal complications due to serum monoclonal protein. Here, we present a case of TIN presumably attributable to AAV with monoclonal gammopathy. Laboratory data revealed acute kidney injury, elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) and ANCA titers, and elevated tubular injury markers. Renal biopsy revealed TIN with no apparent glomerular lesion. The findings of peritubular capillaritis and tubulitis indicated that AAV had contributed to the development of TIN. However, in situ hybridization for free light chains revealed kappa light chain restriction, indicating that the involvement of monoclonal gammopathy in the pathogenesis of TIN remains possible. The patient also developed ophthalmic neuropathy, probably caused by AAV. Oral prednisone (0.6 mg/kg/day) administration improved both the ocular symptoms and the laboratory parameters. Our case demonstrated that the concurrence of AAV and monoclonal gammopathy could pose a diagnostic dilemma in distinguishing the cause of TIN. Besides, some reports suggest an association between AAV and monoclonal gammopathy, although direct evidence is lacking. Further research is needed to establish this association.
Keywords: ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV); Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA); Monoclonal gammopathy; Peritubular capillaritis (PTCitis); Tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN).
© 2021. Japanese Society of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Ohashi N, Ishigaki S, Kitajima K, Tsuji N, Isobe S, Iwakura T, et al. The level of urinary alpha1 microglobulin excretion is a useful marker of peritubular capillaritis in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody associated vasculitis. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2015;19(5):851–858. doi: 10.1007/s10157-014-1073-z. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

