NUAK1 and NUAK2 Fine-Tune TGF-β Signaling
- PMID: 34282782
- PMCID: PMC8268639
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13133377
NUAK1 and NUAK2 Fine-Tune TGF-β Signaling
Abstract
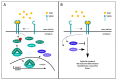
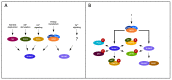
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling plays a key role in governing various cellular processes, extending from cell proliferation and apoptosis to differentiation and migration. Due to this extensive involvement in the regulation of cellular function, aberrant TGF-β signaling is frequently implicated in the formation and progression of tumors. Therefore, a full understanding of the mechanisms of TGF-β signaling and its key components will provide valuable insights into how this intricate signaling cascade can shift towards a detrimental course. In this review, we discuss the interplay between TGF-β signaling and the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-related NUAK kinase family. We highlight the function and regulation of these kinases with focus on the pivotal role NUAK1 and NUAK2 play in regulating TGF-β signaling. Specifically, TGF-β induces the expression of NUAK1 and NUAK2 that regulates TGF-β signaling output in an opposite manner. Besides the focus on the TGF-β pathway, we also present a broader perspective on the expression and signaling interactions of the NUAK kinases to outline the broader functions of these protein kinases.
Keywords: AMPK; LKB1; NUAK1; NUAK2; SMAD; TGF-β.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

