OB-Folds and Genome Maintenance: Targeting Protein-DNA Interactions for Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 34283091
- PMCID: PMC8269290
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13133346
OB-Folds and Genome Maintenance: Targeting Protein-DNA Interactions for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
Genome stability and maintenance pathways along with their requisite proteins are critical for the accurate duplication of genetic material, mutation avoidance, and suppression of human diseases including cancer. Many of these proteins participate in these pathways by binding directly to DNA, and a subset employ oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide binding folds (OB-fold) to facilitate the protein-DNA interactions. OB-fold motifs allow for sequence independent binding to single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) and can serve to position specific proteins at specific DNA structures and then, via protein-protein interaction motifs, assemble the machinery to catalyze the replication, repair, or recombination of DNA. This review provides an overview of the OB-fold structural organization of some of the most relevant OB-fold containing proteins for oncology and drug discovery. We discuss their individual roles in DNA metabolism, progress toward drugging these motifs and their utility as potential cancer therapeutics. While protein-DNA interactions were initially thought to be undruggable, recent reports of success with molecules targeting OB-fold containing proteins suggest otherwise. The potential for the development of agents targeting OB-folds is in its infancy, but if successful, would expand the opportunities to impinge on genome stability and maintenance pathways for more effective cancer treatment.
Keywords: DNA binding; DNA damage response; DNA repair; DNA replication; OB-fold; cancer therapy; drug development; genome stability; single-stranded DNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

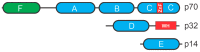
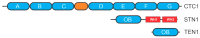



References
-
- Taib N., Gribaldo S., A MacNeill S. Single-Stranded DNA-Binding Proteins in the Archaea. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021;2281:23–47. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

