Anatomical variants of pulmonary segments and uni-portal thoracoscopic segmentectomy for lung cancer in a patient with Kartagener syndrome: a case report
- PMID: 34283387
- PMCID: PMC8416861
- DOI: 10.1007/s11748-021-01685-3
Anatomical variants of pulmonary segments and uni-portal thoracoscopic segmentectomy for lung cancer in a patient with Kartagener syndrome: a case report
Abstract
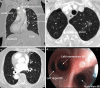
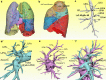
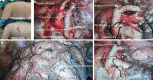
Situs inversus totalis (SIT) is an extremely uncommon congenital disease where the major organs of the body are transposed through the sagittal plane. Kartagener syndrome is a complication of SIT with immotility of bronchial cilia, bronchiectasis, and chronic sinusitis. There is no report describing patients with Kartagener syndrome who accept uni-portal segmentectomies for lung cancer in past studies. Here we report a 74-year-old female patient with both Kartagener syndrome and a small early-stage lung cancer lesion located in the apical segment of the left upper lobe (LS1). The pulmonary segment anatomy of the left upper lobe in this case, which had very rare variants, was presented and interpreted in detail. This patient underwent an anatomic segmentectomy to the LS1 and a partial excision to the left middle lobe with bronchiectasis through a single 3 cm length incision. We believe that the case can give surgeons some experience and inspiration.
Keywords: Anatomic segmentectomy; Kartagener syndrome; Lung cancer; Situs inversus totalis; VATS.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bielewicz M, Wojtyś M, Witkowska D, Alchimowicz J, Wójcik J, Grodzki T. Non-small cell lung cancer in patient with visceral total inversion. Pneumonol Alergol Pol. 2009;77(2):200–204. - PubMed
-
- Nagashima T, Shimizu K, Ohtaki Y, Obayashi K, Kakegawa S, Nakazawa S, et al. An analysis of variations in the bronchovascular pattern of the right upper lobe using three-dimensional CT angiography and bronchography. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;63(6):354–360. doi: 10.1007/s11748-015-0531-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

