How is Etuaptmumk/Two-Eyed Seeing characterized in Indigenous health research? A scoping review
- PMID: 34283831
- PMCID: PMC8291645
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254612
How is Etuaptmumk/Two-Eyed Seeing characterized in Indigenous health research? A scoping review
Erratum in
-
Correction: How is Etuaptmumk/Two-Eyed Seeing characterized in Indigenous health research? A scoping review.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 11;19(7):e0307249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307249. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38990975 Free PMC article.
Abstract
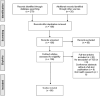
Our scoping review sought to consider how Etuaptmumk or Two-Eyed Seeing is described in Indigenous health research and to compare descriptions of Two-Eyed Seeing between original authors (Elders Albert and Murdena Marshall, and Dr. Cheryl Bartlett) and new authors. Using the JBI scoping review methodology and qualitative thematic coding, we identified seven categories describing the meaning of Two-Eyed Seeing from 80 articles: guide for life, responsibility for the greater good and future generations, co-learning journey, multiple or diverse perspectives, spirit, decolonization and self-determination, and humans being part of ecosystems. We discuss inconsistencies between the original and new authors, important observations across the thematic categories, and our reflections from the review process. We intend to contribute to a wider dialogue about how Two-Eyed Seeing is understood in Indigenous health research and to encourage thoughtful and rich descriptions of the guiding principle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Marshall A, Bartlett C. Two-Eyed Seeing for Knowledge Gardening. Peters MA, editor. Encyclopedia of Educational Philosophy and Theory. Springer online; 2018.
-
- Iwama M, Marshall M, Marshall A, Bartlett C. Two-Eyed Seeing and the Language of Healing in Community-Based Research. Can J Nativ Educ. 2009;32: 3–23,117. Available: http://www.integrativescience.ca/uploads/articles/2009Iwama-etal-CJNE-Tw...
-
- Marshall M, Marshall A, Bartlett C. Two-eyed seeing in medicine. 2nd ed. In: Greenwood M, de Leeuw S, Lindsay N., editors. Determinants of indigenous Health: Beyond the Social. 2nd ed. Canadian Scholars Press; 2018.
-
- Bartlett C., Marshall M., & Marshall A. Integrative Science: Enabling Concepts within a Journey Guided by Trees Holding Hands and Two-Eyed Seeing. Two-Eyed Seeing Knowledge Sharing Series, Manuscript No.1. Sydney, Nova Scotia: Institute for Integrative Science & Health, Cape Breton University; 2007. http://www.integrativescience.ca/uploads/articles/2007-Bartlett-Marshall...
-
- Bartlett C, Marshall M, Marshall A. Two-Eyed Seeing and other Lessons Learned within a co-learning journey of bringing together indigenous and mainstream knowledges and ways of knowing. J Environ Stud. 2012;2: 331–340. doi: 10.1007/s13412-012-0086-8 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources