Effect of beinaglutide treatment on weight loss in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and overweight/obesity
- PMID: 34283904
- PMCID: PMC10522179
- DOI: 10.20945/2359-3997000000388
Effect of beinaglutide treatment on weight loss in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and overweight/obesity
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effect of beinaglutide on weight loss and plasma protein patterns of inflammation/obesity relevant cytokines and biomarkers.
Methods: This study involved 36 adult patients with a body mass index (BMI) of ≥ 24 kg/m2 and T2DM. Beinaglutide was administered for three months. Changes in body weight, fasting plasma glucose (FPG) level, 2 h postprandial plasma glucose (2h-PG) level, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level, BMI and visceral and subcutaneous fat areas were measured at baseline and after three months of treatment. In addition, relevant inflammation/obesity cytokines and biomarkers were measured.
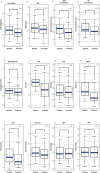
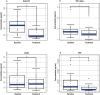
Results: After three months, beinaglutide treatment led to significant changes, including in body weight, BMI, FPG level, HbA1c level, visceral and subcutaneous fat areas. In addition, serpin E1, leptin, C-reaction protein (CRP) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) also decreased significantly. The plasma protein concentrations of CRP (Log2 transformed) were found to be positively correlated with the percentage of weight loss (R = 0.514 and p-value = 0.021).
Conclusion: Beinaglutide treatment resulted in weight loss, plasma glucose control and anti-inflammatory effects in patients with T2DM and overweight/obesity.
Keywords: GLP-1; T2DM; obesity; overweight.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: no potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beinaglutide showed significant weight-loss benefit and effective glycaemic control for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in a real-world setting: a 3-month, multicentre, observational, retrospective, open-label study.Obes Sci Pract. 2019 Jun 17;5(4):366-375. doi: 10.1002/osp4.342. eCollection 2019 Aug. Obes Sci Pract. 2019. PMID: 31452921 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Beinaglutide Versus Metformin for Weight Loss in Overweight and Obese Non-diabetic Patients.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2022 Jun;130(6):358-367. doi: 10.1055/a-1608-0345. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 34856624 Free PMC article.
-
Beinaglutide for weight management in Chinese individuals with overweight or obesity: A phase 3 randomized controlled clinical study.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024 Feb;26(2):690-698. doi: 10.1111/dom.15360. Epub 2023 Nov 9. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024. PMID: 37945546 Clinical Trial.
-
Is Bariatric Surgery Effective for Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Body Mass Index < 35 kg/m2? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Obes Surg. 2021 Sep;31(9):4083-4092. doi: 10.1007/s11695-021-05520-9. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Obes Surg. 2021. PMID: 34244912
-
Efficacy of Metformin Treatment with Respect to Weight Reduction in Children and Adults with Obesity: A Systematic Review.Drugs. 2018 Dec;78(18):1887-1901. doi: 10.1007/s40265-018-1025-0. Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30511324
Cited by
-
The efficacy and safety of beinaglutide alone or in combination with insulin glargine in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who are inadequately controlled with oral antihyperglycemic therapy: A multicenter, open-label, randomized trial.J Diabetes. 2023 Oct 20;16(2):e13483. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13483. Online ahead of print. J Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37864379 Free PMC article.
-
GLP-1 receptor agonists for the treatment of obesity: Role as a promising approach.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 1;14:1085799. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1085799. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36843578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of beinaglutide with continuous subcutaneous infusion in newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, control, open-labeled clinical trial.J Endocrinol Invest. 2025 Jul 28. doi: 10.1007/s40618-025-02665-7. Online ahead of print. J Endocrinol Invest. 2025. PMID: 40719951
-
Effect of beinaglutide combined with metformin versus aspart 30 with metformin on metabolic profiles and antidrug antibodies in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized clinical trial.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Dec 6;14:1267503. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1267503. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38125788 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A narrative review of approved and emerging anti-obesity medications.Saudi Pharm J. 2023 Oct;31(10):101757. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.101757. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Saudi Pharm J. 2023. PMID: 37712012 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gallagher D, Heymsfield SB, Heo M, Jebb SA, Murgatroyd PR, Sakamoto Y. Healthy percentage body fat ranges: an approach for developing guidelines based on body mass index. Am J Clin Nutr . 2000;72(3):694–701. - PubMed
-
- Zhai F, Wang H, Du S, He Y, Wang Z, Ge K, et al. Prospective study on nutrition transition in China. Nutr Rev . 2009;67(Suppl 1):S56–S61. - PubMed
-
- Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration. Wormser D, Kaptoge S, Di Angelantonio E, Wood AM, Pennells L, Thompson A, et al. Separate and combined associations of body-mass index and abdominal adiposity with cardiovascular disease: collaborative analysis of 58 prospective studies. Lancet . 2011;377(9771):1085–1095. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
