SARS-CoV-2 screening: effectiveness and risk of increasing transmission
- PMID: 34283945
- PMCID: PMC8292014
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2021.0164
SARS-CoV-2 screening: effectiveness and risk of increasing transmission
Abstract
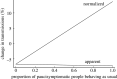
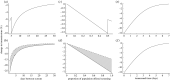
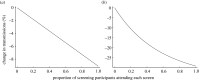
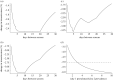
Testing asymptomatic people for SARS-CoV-2 aims to reduce COVID-19 transmission. Screening programmes' effectiveness depends upon testing strategy, sample handling logistics, test sensitivity and individual behaviour, in addition to dynamics of viral transmission. The interaction between these factors is not fully characterized. We investigated the interaction between these factors to determine how to optimize reduction of transmission. We estimate that under idealistic assumptions 70% of transmission may be averted, but under realistic assumptions only 7% may be averted. We show that programmes that overwhelm laboratory capacity or reduce isolation of those with minor symptoms have increased transmission compared with those that do not: programmes need to be designed to avoid these issues, or they will be ineffective or even counter-productive. Our model allows optimal selection of whom to test, quantifies the balance between accuracy and timeliness, and quantifies potential impacts of behavioural interventions. We anticipate our model can be used to understand optimal screening strategies for other infectious diseases with substantially different dynamics.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic; SARS-CoV-2; infection transmission; mass screening.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparing two sample pooling strategies for SARS-CoV-2 RNA detection for efficient screening of COVID-19.J Med Virol. 2021 May;93(5):2805-2809. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26632. Epub 2021 Mar 11. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 33107614
-
Systematic screening on admission for SARS-CoV-2 to detect asymptomatic infections.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2021 Feb 27;10(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13756-021-00912-z. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2021. PMID: 33640031 Free PMC article.
-
[SARS-CoV-2 and Microbiological Diagnostic Dynamics in COVID-19 Pandemic].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2020 Jul;54(3):497-509. doi: 10.5578/mb.69839. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2020. PMID: 32755524 Review. Turkish.
-
Preventing and Mitigating SARS-CoV-2 Transmission - Four Overnight Camps, Maine, June-August 2020.MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020 Sep 4;69(35):1216-1220. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6935e1. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020. PMID: 32881850 Free PMC article.
-
Thoracic imaging tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 30;9:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 26;11:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub3. PMID: 32997361 Updated.
Cited by
-
Non-pharmaceutical interventions to reduce COVID-19 transmission in the UK: a rapid mapping review and interactive evidence gap map.J Public Health (Oxf). 2024 May 29;46(2):e279-e293. doi: 10.1093/pubmed/fdae025. J Public Health (Oxf). 2024. PMID: 38426578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modelling the impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions on workplace transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in the home-delivery sector.PLoS One. 2023 May 5;18(5):e0284805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284805. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37146037 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling the impact of repeat asymptomatic testing policies for staff on SARS-CoV-2 transmission potential.J Theor Biol. 2023 Jan 21;557:111335. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2022.111335. Epub 2022 Nov 2. J Theor Biol. 2023. PMID: 36334850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dora AV, Winnett A, Jatt LP, Davar K, Watanabe M, Sohn L, Kern HS, Graber CJ, Goetz MB. 2020. Universal and serial laboratory testing for SARS-CoV-2 at a long-term care skilled nursing facility for veterans—Los Angeles, California, 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep. 69, 651-655. (10.15585/mmwr.mm6921e1) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kissler SM et al. 2020. Viral dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 infection and the predictive value of repeat testing. medRxiv. (10.1101/2020.10.21.20217042) - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

