Efficacy of immunohistochemical staining in detecting <em>Helicobacter pylori</em> in Saudi patients with minimal and atypical infection
- PMID: 34284564
- PMCID: PMC8314390
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2021.3222
Efficacy of immunohistochemical staining in detecting <em>Helicobacter pylori</em> in Saudi patients with minimal and atypical infection
Abstract
Gastric Helicobacter pylori infection is diagnosed based on histopathological evaluation of gastric mucosal biopsies, urease test, urea breath test, H. pylori culturing, or direct detection using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of immunohistochemical (IHC) staining in detecting H. pylori in gastric biopsies from patients with chronic gastritis and minimal or atypical infection. Gastric biopsies from 50 patients with chronic gastritis were subjected to routine haematoxylin and eosin (H-E), modified Giemsa, and IHC staining. The results of staining were compared with those of quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). The qRT-PCR analysis identified 32 (64%) H. pylori-positive cases, whereas IHC, H-E, and modified Giemsa staining identified 29 (58%), 27 (54%), and 21 (42%) positive cases. The sensitivity of IHC staining (87.50%) was higher than that of H-E (59.38%) and modified Giemsa (43.75%) staining. The specificity of H-E, modified Giemsa, and IHC staining was 55.56%, 61.11%, and 94.44%, respectively. IHC staining exhibited the highest diagnostic accuracy (90%), followed by H-E (58%) and modified Giemsa (50%) staining. Active gastritis, intestinal metaplasia, and lymphoid follicles were detected in 32 (64%), 4 (8%), and 22 (44%) cases, respectively, and all of these cases were H. pylori positive. In contrast to routine H-E and modified Giemsa staining, IHC allows for the accurate H. pylori detection in cases with minimal or atypical infection. Moreover, IHC can be an alternative diagnostic method to qRT-PCR for detection of H. pylori in such cases.
Figures
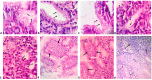
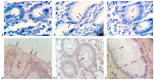
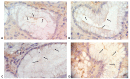
References
-
- Shimizu T, Akamatsu T, Ota H, Katsuyama T. Immunohistochemical detection of Helicobacter pylori in the surface mucous gel layer and its clinicopathological significance. Helicobacter 1996;1:197-206. - PubMed
-
- Saniee P, Shahreza S, Siavoshi F. Negative effect of protonpump inhibitors (PPIs) on Helicobacter pylori growth, morphology, and urease test and recovery after PPI removal--An in vitro study. Helicobacter 2016;21143-52. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

