TRIM27 interacts with Iκbα to promote the growth of human renal cancer cells through regulating the NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 34284744
- PMCID: PMC8293539
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08562-5
TRIM27 interacts with Iκbα to promote the growth of human renal cancer cells through regulating the NF-κB pathway
Abstract
Background: The tripartite motif (TRIM) family proteins exhibit oncogenic roles in various cancers. The roles of TRIM27, a member of the TRIM super family, in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) remained unexplored. In the current study, we aimed to investigate the clinical impact and roles of TRIM27 in the development of RCC.
Methods: The mRNA levels of TRIM27 and Kaplan-Meier survival of RCC were analyzed from The Cancer Genome Atlas database. Real-time PCR and Western blotting were used to measure the mRNA and protein levels of TRIM27 both in vivo and in vitro. siRNA and TRIM27 were exogenously overexpressed in RCC cell lines to manipulate TRIM27 expression.
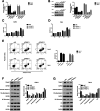
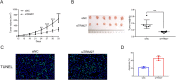
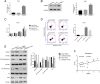
Results: We discovered that TRIM27 was elevated in RCC patients, and the expression of TRIM27 was closely correlated with poor prognosis. The loss of function and gain of function results illustrated that TRIM27 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in RCC cell lines. Furthermore, TRIM27 expression was positively associated with NF-κB expression in patients with RCC. Blocking the activity of NF-κB attenuated the TRIM27-mediated enhancement of proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis. TRIM27 directly interacted with Iκbα, an inhibitor of NF-κB, to promote its ubiquitination, and the inhibitory effects of TRIM27 on Iκbα led to NF-κB activation.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that TRIM27 exhibits an oncogenic role in RCC by regulating NF-κB signaling. TRIM27 serves as a specific prognostic indicator for RCC, and strategies targeting the suppression of TRIM27 function may shed light on future therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Iκbα; NF-κB; Proliferation; Renal cell carcinoma; TRIM27.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 53 inhibits the occurrence and development of clear cell renal cell carcinoma through NF-κB pathway inactivation.Cancer Med. 2021 Jun;10(11):3674-3688. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3911. Epub 2021 May 11. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 33973730 Free PMC article.
-
Decitabine induces G2/M cell cycle arrest by suppressing p38/NF-κB signaling in human renal clear cell carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Sep 1;8(9):11140-8. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26617834 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction of YBX1 with G3BP1 promotes renal cell carcinoma cell metastasis via YBX1/G3BP1-SPP1- NF-κB signaling axis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Sep 3;38(1):386. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1347-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31481087 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular mechanism of NF-κB dysregulation across different subtypes of renal cell carcinoma.J Adv Res. 2025 Jun;72:501-514. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.07.030. Epub 2024 Jul 31. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 39094893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of nuclear factor kappa B in renal cell carcinoma.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011 Nov;43(11):1537-49. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2011.08.003. Epub 2011 Aug 12. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21854869 Review.
Cited by
-
Small and mighty - microRNAs pulling the strings.Biomed J. 2022 Dec;45(6):851-856. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2022.11.003. Epub 2022 Nov 26. Biomed J. 2022. PMID: 36442792 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM Proteins: Key Regulators of Immunity to Herpesvirus Infection.Viruses. 2024 Nov 6;16(11):1738. doi: 10.3390/v16111738. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39599852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of SUMO E3 Ligases in Signaling Pathway of Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 26;23(7):3639. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073639. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Gene Signature of Tripartite Motif Family for Predicting the Prognosis in Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma and Its Association With Immune Cell Infiltration.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 17;12:840410. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.840410. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35371994 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-Associated Dysregulation of Sumo Regulators: Proteases and Ligases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 20;23(14):8012. doi: 10.3390/ijms23148012. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887358 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

