Oxidative stress tolerance contributes to heterologous protein production in Pichia pastoris
- PMID: 34284814
- PMCID: PMC8290557
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-021-02013-w
Oxidative stress tolerance contributes to heterologous protein production in Pichia pastoris
Abstract
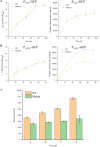
Background: Pichia pastoris (syn. Komagataella phaffii) is an important yeast system for heterologous protein expression. A robust P. pastoris mutant with oxidative and thermal stress cross-tolerance was acquired in our previous study. The robust mutant can express a 2.5-fold higher level of lipase than its wild type (WT) under methanol induction conditions.
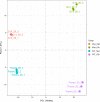
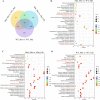
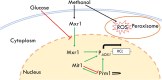
Results: In this study, we found that the robust mutant not only can express a high level of lipase, but also can express a high level of other heterogeneous proteins (e.g., green fluorescence protein) under methanol induction conditions. Additionally, the intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in the robust mutant were lower than that in the WT under methanol induction conditions. To figure out the difference of cellular response to methanol between the WT and the robust mutant, RNA-seq was detected and compared. The results of RNA-seq showed that the expression levels of genes related to antioxidant, MAPK pathway, ergosterol synthesis pathway, transcription factors, and the peroxisome pathway were upregulated in the robust mutant compared to the WT. The upregulation of these key pathways can improve the oxidative stress tolerance of strains and efficiently eliminate cellular ROS. Hence, we inferred that the high heterologous protein expression efficiency in the robust mutant may be due to its enhanced oxidative stress tolerance. Promisingly, we have indeed increased the expression level of lipase up to 1.6-fold by overexpressing antioxidant genes in P. pastoris.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated the impact of methanol on the expression levels of genes in P. pastoris and emphasized the contribution of oxidative stress tolerance on heterologous protein expression in P. pastoris. Our results shed light on the understanding of protein expression mechanism in P. pastoris and provided an idea for the rational construction of robust yeast with high expression ability.
Keywords: Heterologous protein expression; Lipase; Oxidative stress tolerance; Pichia pastoris; Yeast.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of Pichia pastoris (Komagataella phaffii) GS115 During Heterologous Protein Production Using a High-Cell-Density Fed-Batch Cultivation Strategy.Front Microbiol. 2020 Mar 20;11:463. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00463. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32265887 Free PMC article.
-
Augmented peroxisomal ROS buffering capacity renders oxidative and thermal stress cross-tolerance in yeast.Microb Cell Fact. 2021 Jul 12;20(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12934-021-01623-1. Microb Cell Fact. 2021. PMID: 34247591 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics and transcriptomics of Pichia pastoris.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 5;17:550. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2876-y. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27495311 Free PMC article.
-
Rational development of bioprocess engineering strategies for recombinant protein production in Pichia pastoris (Komagataella phaffii) using the methanol-free GAP promoter. Where do we stand?N Biotechnol. 2019 Nov 25;53:24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2019.06.002. Epub 2019 Jun 10. N Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31195158 Review.
-
Heterologous Protein Expression in Pichia pastoris: Latest Research Progress and Applications.Chembiochem. 2018 Jan 4;19(1):7-21. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201700460. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Chembiochem. 2018. PMID: 29235217 Review.
Cited by
-
Scalable, methanol-free manufacturing of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain in engineered Komagataella phaffii.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2022 Feb;119(2):657-662. doi: 10.1002/bit.27979. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2022. PMID: 34780057 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and scale-up production of recombinant human papillomavirus type 52 L1 protein in methylotrophic yeast Hansenula polymorpha.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2024 Mar;22(1):100342. doi: 10.1016/j.jgeb.2023.100342. Epub 2024 Feb 12. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38494245 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic engineering of Komagataella phaffii for the efficient utilization of methanol.Microb Cell Fact. 2024 Jul 17;23(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02475-1. Microb Cell Fact. 2024. PMID: 39014373 Free PMC article.
-
Balancing Doses of EL222 and Light Improves Optogenetic Induction of Protein Production in Komagataella phaffii.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2025 Sep;122(9):2478-2498. doi: 10.1002/bit.29027. Epub 2025 May 24. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2025. PMID: 40411288 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of reference genes for transcript analyses in Komagataella phaffii (Pichia pastoris).Fungal Biol Biotechnol. 2023 Mar 29;10(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s40694-023-00154-1. Fungal Biol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36991508 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
- 2021YFC2100203/national key research and development program of china
- 31671799/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32072162/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- KYCX18_1791/Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province
- LITE2018-09/National First-Class Discipline Program of Light Industry Technology and Engineering
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

