Implementation and implications for polygenic risk scores in healthcare
- PMID: 34284826
- PMCID: PMC8290135
- DOI: 10.1186/s40246-021-00339-y
Implementation and implications for polygenic risk scores in healthcare
Abstract
Increasing amounts of genetic data have led to the development of polygenic risk scores (PRSs) for a variety of diseases. These scores, built from the summary statistics of genome-wide association studies (GWASs), are able to stratify individuals based on their genetic risk of developing various common diseases and could potentially be used to optimize the use of screening and preventative treatments and improve personalized care for patients. Many challenges are yet to be overcome, including PRS validation, healthcare professional and patient education, and healthcare systems integration. Ethical challenges are also present in how this information is used and the current lack of diverse populations with PRSs available. In this review, we discuss the topics above and cover the nature of PRSs, visualization schemes, and how PRSs can be improved. With these tools on the horizon for multiple diseases, scientists, clinicians, health systems, regulatory bodies, and the public should discuss the uses, benefits, and potential risks of PRSs.
Keywords: Clinical genetics; Genetic risk; PRS; Polygenic risk score; Public health; Risk stratification.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

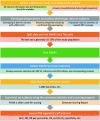


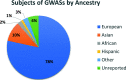
References
-
- Agerbo E, Sullivan PF, Vilhjalmsson BJ, Pedersen CB, Mors O, Børglum AD, Hougaard DM, Hollegaard MV, Meier S, Mattheisen M. Polygenic risk score, parental socioeconomic status, family history of psychiatric disorders, and the risk for schizophrenia: a Danish population-based study and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiat. 2015;72(7):635–641. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.0346. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

