Economic and social impacts of COVID-19 and public health measures: results from an anonymous online survey in Thailand, Malaysia, the UK, Italy and Slovenia
- PMID: 34285007
- PMCID: PMC8295020
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-046863
Economic and social impacts of COVID-19 and public health measures: results from an anonymous online survey in Thailand, Malaysia, the UK, Italy and Slovenia
Abstract
Objectives: To understand the impact of COVID-19 and public health measures on different social groups, we conducted a mixed-methods study in five countries ('SEBCOV-social, ethical and behavioural aspects of COVID-19'). Here, we report the results of the online survey.
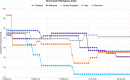
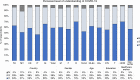
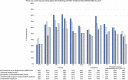
Study design and statistical analysis: Overall, 5058 respondents from Thailand, Malaysia, the UK, Italy and Slovenia completed the self-administered survey between May and June 2020. Poststratification weighting was applied, and associations between categorical variables assessed. Frequency counts and percentages were used to summarise categorical data. Associations between categorical variables were assessed using Pearson's χ2 test. Data were analysed in Stata 15.0 RESULTS: Among the five countries, Thai respondents reported having been most, and Slovenian respondents least, affected economically. The following factors were associated with greater negative economic impacts: being 18-24 years or 65 years or older; lower education levels; larger households; having children under 18 in the household and and having flexible/no income. Regarding social impact, respondents expressed most concern about their social life, physical health, mental health and well-being.There were large differences between countries in terms of voluntary behavioural change, and in compliance and agreement with COVID-19 restrictions. Overall, self-reported compliance was higher among respondents who self-reported a high understanding of COVID-19. UK respondents felt able to cope the longest and Thai respondents the shortest with only going out for essential needs or work. Many respondents reported seeing news perceived to be fake, the proportion varying between countries, with education level and self-reported levels of understanding of COVID-19.
Conclusions: Our data showed that COVID-19 and public health measures have uneven economic and social impacts on people from different countries and social groups. Understanding the factors associated with these impacts can help to inform future public health interventions and mitigate their negative consequences.
Trial registration number: TCTR20200401002.
Keywords: epidemiology; public health.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . Non-pharmaceutical public health measures for mitigating the risk and impact of epidemic and pandemic influenza, 2019. Available: https://www.who.int/influenza/publications/public_health_measures/public... [Accessed 9 Oct 2020].
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs), 2020. Available: https://www.cdc.gov/nonpharmaceutical-interventions/index.html [Accessed 17 Jul 2020].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
