Clinicopathological Study of Intradural Extramedullary Spinal Tumors and Its Correlation With Functional Outcome
- PMID: 34285844
- PMCID: PMC8286542
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.15733
Clinicopathological Study of Intradural Extramedullary Spinal Tumors and Its Correlation With Functional Outcome
Abstract
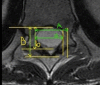
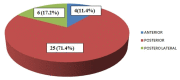
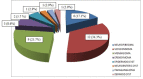
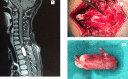
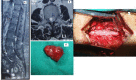
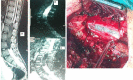
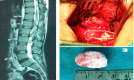
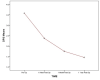
Introduction Intradural extramedullary (IDEM) spinal cord tumors account for approximately two-thirds of largely benign intraspinal neoplasms. These are amenable to gross total excision and usually carry a good functional outcome. Methods In this study, we reviewed the surgical outcomes of 35 patients who underwent excision of intradural extramedullary tumors. Patient demographics, severity and duration of symptoms, and tumor characteristics (anatomical and pathological) in all operated spinal IDEM tumors were collected. The neurological findings obtained during the preoperative stage and the postoperative follow-up were evaluated according to the Frankel and Nurick grading. The back pain was assessed with help of the Denis pain scale (DPS). Results The histopathological outcomes of the study were as follows: six patients of neurofibroma, 12 cases of schwannoma, nine cases of meningiomas, three cases of ependymoma, one case of dorsal neurenteric cyst, two cases of epidermoid cyst, one case of cauda equina paraganglioma, and one case of filum terminale dermoid cyst. Paresthesia/numbness were the commonest symptoms (88.6%), weakness of limbs in (80%), sphincter dysfunction in 15 patients (42.9%), and paraplegia was seen in three patients (8.57%). The complications encountered were - one case each of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak, surgical site infection, and pseudomeningocele. The percentage of spinal canal occupied ranged from 71-94%. The mean percentage of the spinal canal occupied by the tumor was 81.8%. In our series, 77.14% of patients (p<0.0001) had good functional outcomes as per improvement in Frankel score. The DPS and Nurick score mean values showed a significant decrease over the follow-up duration as compared to preoperative mean values. Significant functional improvement was noted at the one-week, one-month, and one-year follow-up, with a p-value of <0.0001. Conclusions The IDEM tumors are usually benign and are readily detected by contrast-enhanced MRI scans. These have excellent surgical outcomes with some exceptions. Greater canal occupancy and a longer duration of symptoms are usually seen to correspond with suboptimal functional outcomes.
Keywords: denis pain scale; frankel grade; functional outcome; intradural extramedullary spine tumors; nurick grade.
Copyright © 2021, Narayan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functional outcomes in intradural extramedullary spinal tumors.Surg Neurol Int. 2024 Apr 5;15:114. doi: 10.25259/SNI_689_2023. eCollection 2024. Surg Neurol Int. 2024. PMID: 38742010 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical outcome of intradural extramedullary spinal cord tumors: A single-center retrospective analytical study.Surg Neurol Int. 2021 Apr 8;12:145. doi: 10.25259/SNI_839_2020. eCollection 2021. Surg Neurol Int. 2021. PMID: 33948315 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Surgical Technique and Outcome of the Thoracic and Lumbar Intradural Spinal Tumor Excision Using Minimally Invasive Tubular Retractor System.Asian J Neurosurg. 2019 Apr-Jun;14(2):453-460. doi: 10.4103/ajns.AJNS_254_18. Asian J Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31143261 Free PMC article.
-
A rare case of intradural and extramedullary epidermoid cyst after repetitive epidural anesthesia: case report and review of the literature.World J Surg Oncol. 2017 Jul 17;15(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12957-017-1186-4. World J Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28716031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intradural Extramedullary Spinal Neoplasms: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation.Radiographics. 2019 Mar-Apr;39(2):468-490. doi: 10.1148/rg.2019180200. Radiographics. 2019. PMID: 30844353 Review.
Cited by
-
Intradural extra-medullary spinal cord tumor after dorso-lumbar spine fixation following 12th dorsal vertebra burst fracture: A case report with literature review.Radiol Case Rep. 2024 Dec 18;20(3):1393-1397. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2024.11.080. eCollection 2025 Mar. Radiol Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39801524 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal Cord Tumors: A Review of Demographic Characteristics and Treatment Follow-Up of Patients in Isfahan City, Iran.Adv Biomed Res. 2023 Oct 28;12:239. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_168_23. eCollection 2023. Adv Biomed Res. 2023. PMID: 38073727 Free PMC article.
-
Adult cervicothoracic subpial fibrolipoma without dysraphism: An extremely rare case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023 Aug;109:108616. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108616. Epub 2023 Aug 3. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37544094 Free PMC article.
-
Functional outcomes in intradural extramedullary spinal tumors.Surg Neurol Int. 2024 Apr 5;15:114. doi: 10.25259/SNI_689_2023. eCollection 2024. Surg Neurol Int. 2024. PMID: 38742010 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal Meningioma Surgery through the Ages-Single-Center Experience over Three Decades.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Oct 28;58(11):1549. doi: 10.3390/medicina58111549. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36363510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Intradural spinal tumors: current classification and MRI features. Abul-Kasim K, Thurnher MM, McKeever P, Sundgren PC. Neuroradiology. 2008;50:301–314. - PubMed
-
- Primary intraspinal neoplasms in Norway, 1955 to 1986: a population-based survey of 467 patients. Helseth A, Mørk SJ. J Neurosurg. 1989;71:842–845. - PubMed
-
- Nittner K. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. New York: Elsevier; 1976. Spinal meningiomas, neurinomas, neurofibromas and hourglass tumors; pp. 177–322.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
