Intracellular and Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Measurement in Primary Cultured Neurons
- PMID: 34285985
- PMCID: PMC8275304
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2871
Intracellular and Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Measurement in Primary Cultured Neurons
Abstract
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are chemically reactive oxygen containing molecules. ROS consist of radical oxygen species including superoxide anion (O2 •-) and hydroxyl radical (•OH) and non-radical oxygen species such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), singlet oxygen (O2). ROS are generated by mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, environmental stresses including UV or heat exposure, and cellular responses to xenobiotics ( Ray et al., 2012 ). Excessive ROS production over cellular antioxidant capacity induces oxidative stress which results in harmful effects such as cell and tissue damage. Sufficient evidence suggests that oxidative stresses are involved in cancers, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson disease (Waris and Ahsan, 2006). Though excessive level of ROS triggers detrimental effects, ROS also have been implicated to regulate cellular processes. Since ROS function is context dependent, measurement of ROS level is important to understand cellular processes (Finkel, 2011). This protocol describes how to detect intracellular and mitochondrial ROS in live cells using popular chemical fluorescent dyes.
Keywords: CM-H2DCFDA; Intracellular ROS; MitoSOX; Primary neuron; Reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Copyright © 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
Figures


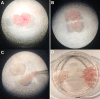

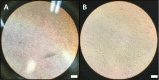



References
-
- Baek S. H., Park S. J., Jeong J. I., Kim S. H., Han J., Kyung J. W., Baik S. H., Choi Y., Choi B. Y., Park J. S., Bahn G., Shin J. H., Jo D. S., Lee J. Y., Jang C. G., Arumugam T. V., Kim J., Han J. W., Koh J. Y., Cho D. H. and Jo D. G.(2017). Inhibition of Drp1 ameliorates synaptic depression, Aβ deposition, and cognitive impairment in an Alzheimer's disease model. J Neurosci 37(20): 5099-5110. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brieger K., Schiavone S., Miller F. J. Jr.and Krause K. H.(2012). Reactive oxygen species: from health to disease. Swiss Med Wkly 142: w13659. - PubMed
-
- Datta K., Sinha S. and Chattopadhyay P.(2000). Reactive oxygen species in health and disease. Natl Med J India 13(6): 304-310. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

