Cobblestone Area-forming Cell Assay of Mouse Bone Marrow Hematopoietic Stem Cells
- PMID: 34286035
- PMCID: PMC8275301
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2824
Cobblestone Area-forming Cell Assay of Mouse Bone Marrow Hematopoietic Stem Cells
Abstract
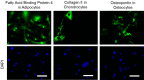
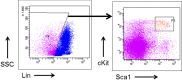
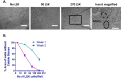
Bone Marrow Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs) require bone marrow microenvironment for their maintenance and proliferation. Culture of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs) provides appropriate environmental signals for HSCs survival in vitro. Here, we provide a detailed protocol that describes culture conditions for MSCs, flow cytometric isolation of HSCs from mouse bone marrow, and perform co-culture of MSCs and HSCs known as Cobblestone area-forming cell (CAFC) assay. Altogether, CAFC assays can be used as a high-throughput in vitro screening model where efforts are made to understand and develop therapies for complex bone marrow diseases. This protocol needs 3 to 4 weeks starting from culturing MSCs, isolating LSK cells (HSCs), and to performing limited dilution CAFC assay.
Keywords: Co-culture assay; Cobblestone area-forming cell assay; Hematopoietic Stem Cells; Mesenchymal Stromal Cells.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chimeric feeders of mesenchymal stromal cells and stromal cells modified with constitutively active AKT expand hematopoietic stem cells.Regen Med. 2019 Jun;14(6):535-553. doi: 10.2217/rme-2018-0157. Epub 2019 May 22. Regen Med. 2019. PMID: 31115264
-
Quantitation of murine hematopoietic stem cells in vitro by limiting dilution analysis of cobblestone area formation on a clonal stromal cell line.Exp Hematol. 1993 Mar;21(3):438-43. Exp Hematol. 1993. PMID: 8440341
-
Use of limiting-dilution type long-term marrow cultures in frequency analysis of marrow-repopulating and spleen colony-forming hematopoietic stem cells in the mouse.Blood. 1991 Nov 15;78(10):2527-33. Blood. 1991. PMID: 1824250
-
Do microRNAs regulate bone marrow stem cell niche physiology?Gene. 2012 Apr 10;497(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.01.045. Epub 2012 Jan 28. Gene. 2012. PMID: 22306262 Review.
-
Adult bone marrow stem cells for cell and gene therapies: implications for greater use.J Cell Biochem Suppl. 2002;38:20-8. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10127. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 2002. PMID: 12046846 Review.
References
-
- de Haan G. and Ploemacher R.(2002). The cobblestone-area-forming cell assay. In: Hematopoietic Stem Cell Protocols. In: Klug, C. A. and Jordan, C. T.(Eds). Humana Press, Totowa 143-151. - PubMed
-
- Denning-Kendall P., Singha S., Bradley B. and Hows J.(2003). Cobblestone area-forming cells in human cord blood are heterogeneous and differ from long-term culture-initiating cells. Stem Cells 21(6): 694-701. - PubMed
-
- Dominici M., Le Blanc K., Mueller I., Slaper-Cortenbach I., Marini F., Krause D., Deans R., Keating A., Prockop D. and Horwitz E.(2006). Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 8(4): 315-317. - PubMed
-
- Hartwell K. A., Miller P. G., Mukherjee S., Kahn A. R., Stewart A. L., Logan D. J., Negri J. M., Duvet M., Jaras M., Puram R., Dancik V., Al-Shahrour F., Kindler T., Tothova Z., Chattopadhyay S., Hasaka T., Narayan R., Dai M., Huang C., Shterental S., Chu L. P., Haydu J. E., Shieh J. H., Steensma D. P., Munoz B., Bittker J. A., Shamji A. F., Clemons P. A., Tolliday N. J., Carpenter A. E., Gilliland D. G., Stern A. M., Moore M. A. S., Scadden D. T., Schreiber S. L., Ebert B. L. and Golub T. R.(2013). Niche-based screening identifies small-molecule inhibitors of leukemia stem cells. Nat Chem Biol 9(12): 840-848. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

