Estimates of Toxoplasmosis Incidence Based on Healthcare Claims Data, Germany, 2011-2016
- PMID: 34286687
- PMCID: PMC8314822
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2708.203740
Estimates of Toxoplasmosis Incidence Based on Healthcare Claims Data, Germany, 2011-2016
Abstract
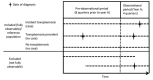
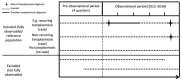
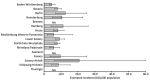
Toxoplasmosis is a zoonotic infection contracted through Toxoplasma gondii-contaminated food, soil, or water. Seroprevalence in Germany is high, but estimates of disease incidence are scarce. We investigated incidences for various toxoplasmosis manifestations using anonymized healthcare claims data from Germany for 2011-2016. Patients with a toxoplasmosis diagnosis during the annual observational period were considered incident. The estimated incidence was adjusted to the general population age/sex distribution. We estimated an annual average of 8,047 toxoplasmosis patients in Germany. The average incidence of non-pregnancy-associated toxoplasmosis patients was 9.6/100,000 population. The incidence was highest in 2011, at 10.6 (95% CI 9.4-12.6)/100,000 population, and lowest in 2016, at 8.0 (95% CI 7.0-9.4)/100,000 population. The average incidence of toxoplasmosis during pregnancy was 40.3/100,000 pregnancies. We demonstrate a substantial toxoplasmosis disease burden in Germany. Public health and food safety authorities should implement toxoplasmosis-specific prevention programs.
Keywords: Germany; Toxoplasma gondii; food safety; healthcare claims data; incidence; parasites; toxoplasmosis; zoonoses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Seroprevalence and risk factors of Toxoplasma gondii infections among high-risk populations in Changzhou City].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2020 Jul 29;32(6):635-639. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2019282. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33325201 Chinese.
-
Unpasteurised milk consumption as a potential risk factor for toxoplasmosis in females with recurrent pregnancy loss.J Obstet Gynaecol. 2020 Nov;40(8):1106-1110. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2019.1702630. Epub 2020 Feb 4. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2020. PMID: 32013639
-
The global seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in pigs: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Vet Parasitol. 2019 May;269:42-52. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Vet Parasitol. 2019. PMID: 31079827
-
Seroepidemiology of Toxoplasma infection in a metropolitan region of Brazil.Epidemiol Infect. 2009 Dec;137(12):1809-15. doi: 10.1017/S0950268809002799. Epub 2009 May 27. Epidemiol Infect. 2009. PMID: 19470195
-
Is the incidence of congenital toxoplasmosis declining?Trends Parasitol. 2023 Jan;39(1):26-37. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2022.10.003. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Trends Parasitol. 2023. PMID: 36400672 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Ocular Toxoplasmosis in Romania: History, Epidemiology, and Public Health: A Narrative Review.Microorganisms. 2024 Jul 27;12(8):1541. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081541. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Pregnancy - Recommendations of the Working Group on Obstetrics and Prenatal Medicine (AGG - Section on Maternal Disorders).Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2023 Sep 18;83(12):1431-1445. doi: 10.1055/a-2111-7394. eCollection 2023 Dec. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2023. PMID: 38046526 Free PMC article.
-
Age and ocular toxoplasmosis: a narrative review.FEMS Microbes. 2025 Feb 26;6:xtaf002. doi: 10.1093/femsmc/xtaf002. eCollection 2025. FEMS Microbes. 2025. PMID: 40098631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA mmu-miR-511-5p: A promising Diagnostic Biomarker in Experimental Toxoplasmosis Using Different Strains and Infective Doses in Mice with Different Immune States Before and After Treatment.Acta Parasitol. 2024 Jun;69(2):1253-1266. doi: 10.1007/s11686-024-00851-w. Epub 2024 May 14. Acta Parasitol. 2024. PMID: 38743178 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of potent anti-toxoplasmosis drugs from secondary metabolites in Citrus limon (lemon) leaves, supported in-silico study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 3;15(1):624. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82787-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39753625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Robert Koch-Institut. RKI guide: toxoplasmosis. 2018. [cited 2021 Jun 21]. https://www.rki.de/DE/Content/Infekt/EpidBull/Merkblaetter/Ratgeber_Toxo...
-
- Hofhuis A, van Pelt W, van Duynhoven YT, Nijhuis CD, Mollema L, van der Klis FR, et al. Decreased prevalence and age-specific risk factors for Toxoplasma gondii IgG antibodies in The Netherlands between 1995/1996 and 2006/2007. Epidemiol Infect. 2011;139:530–8. 10.1017/S0950268810001044 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

