Comparison of Lyme Disease in the United States and Europe
- PMID: 34286689
- PMCID: PMC8314816
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2708.204763
Comparison of Lyme Disease in the United States and Europe
Abstract
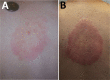
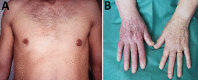
Lyme disease, or Lyme borreliosis, is the most common tickborne disease in the United States and Europe. In both locations, Ixodes species ticks transmit the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato bacteria species responsible for causing the infection. The diversity of Borrelia species that cause human infection is greater in Europe; the 2 B. burgdorferi s.l. species collectively responsible for most infections in Europe, B. afzelii and B. garinii, are not found in the United States, where most infections are caused by B. burgdorferi sensu stricto. Strain differences seem to explain some of the variation in the clinical manifestations of Lyme disease, which are both minor and substantive, between the United States and Europe. Future studies should attempt to delineate the specific virulence factors of the different species of B. burgdorferi s.l. responsible for these variations in clinical features.
Keywords: Borrelia burgdorferi; Borrelia burgdorferi group; Europe; Lyme borreliosis; Lyme disease; Lyme disease spirochete; United States; bacteria; tick-borne diseases; vector-borne infections.
Figures

References
-
- Barbour AG, Gupta RS. The Family Borreliaceae (Spirochaetales), a diverse group in two genera of tick-borne spirochetes of mammals, birds, and reptiles. J Med Entomol. 2021:tjab055. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

